Coenzyme Q redox signalling and longevity
Filippo Scialo Free Radical Biology and Medicine Volume 164, 20 February 2021, Pages 187-205
Highlights
• mtROS are redox messengers that participate in cellular processes ranging from differentiation to tissue homeostasis.
• Most mtROS are produced by CI and CIII. CI/CIII ROS regulate specific physiological and pathological processes.
• The redox state of the Coenzyme Q pool determines electron leak and mtROS production by CI and CIII.
• Defective mitochondria produce high amounts of mtROS, causing oxidative damage and altering redox signalling.
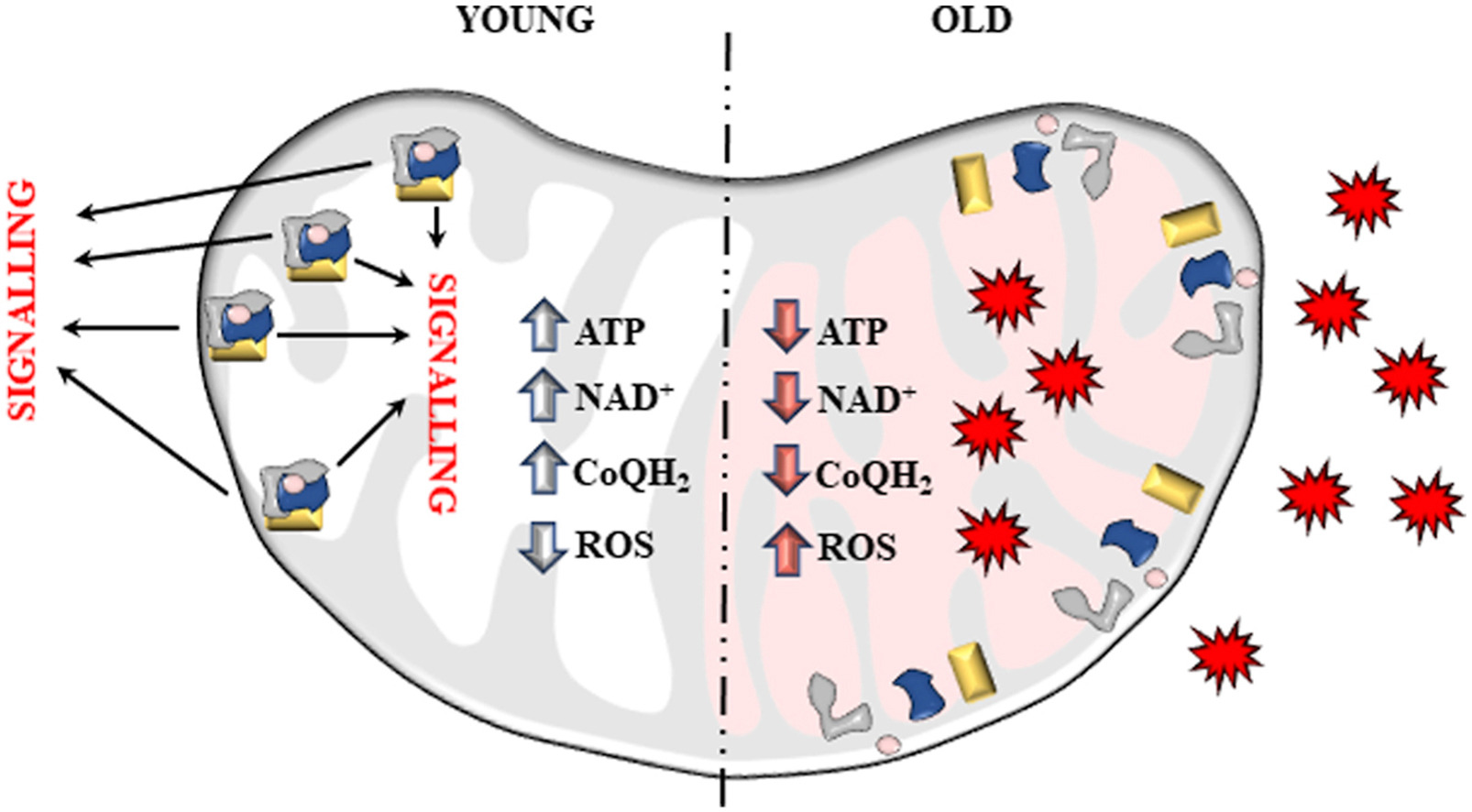
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They produce a significant amount of the energy we need to grow, survive and reproduce. The same system that generates energy in the form of ATP also produces Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (mtROS) were considered for many years toxic by-products of metabolism, responsible for ageing and many degenerative diseases.
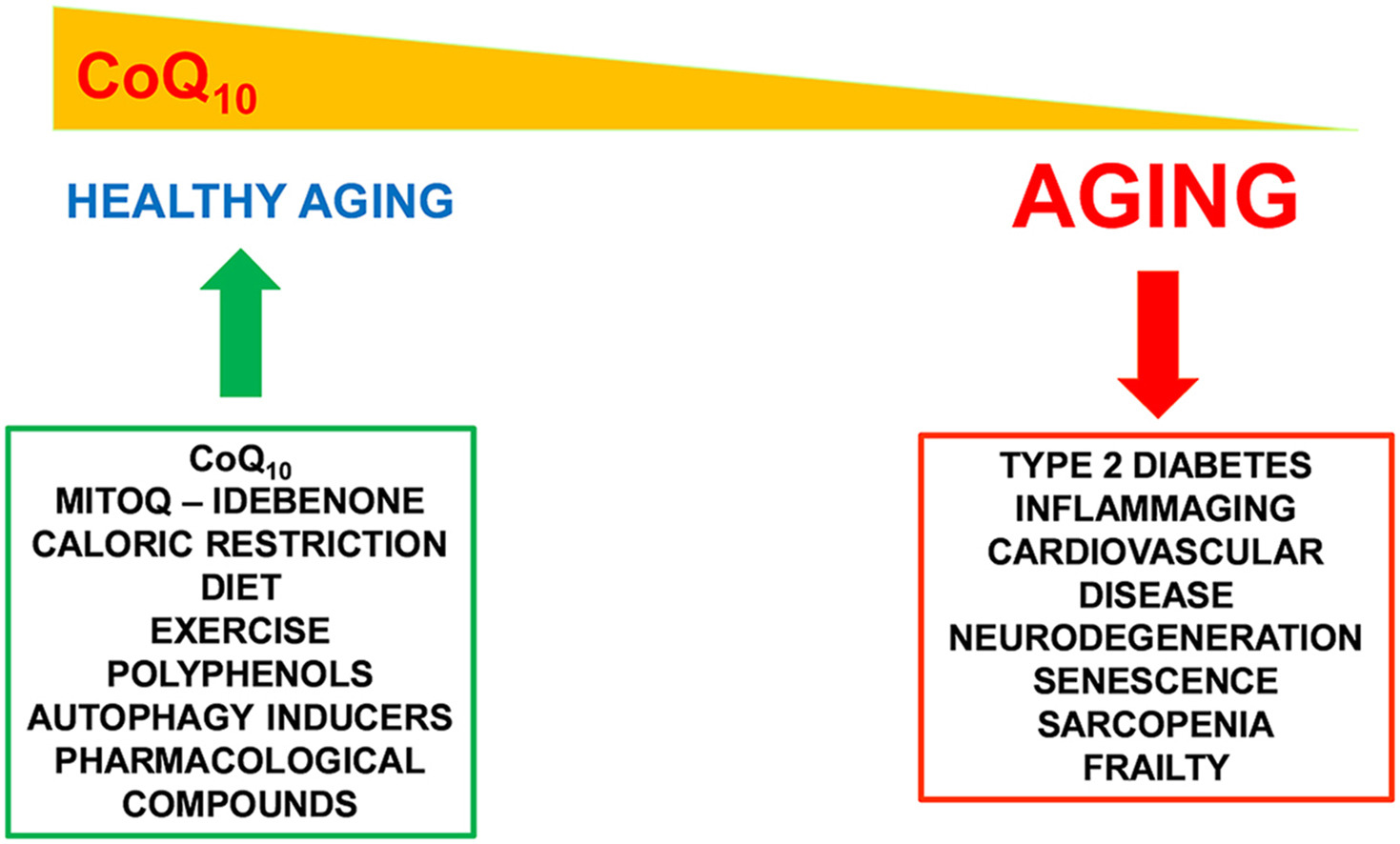
Today, we know that mtROS are essential redox messengers required to determine cell fate and maintain cellular homeostasis. Most mtROS are produced by respiratory complex I (CI) and complex III (CIII). How and when CI and CIII produce ROS is determined by the redox state of the Coenzyme Q (CoQ) pool and the proton motive force (pmf) generated during respiration. During ageing, there is an accumulation of defective mitochondria that generate high levels of mtROS. This causes oxidative stress and disrupts redox signalling.
Here, we review how mtROS are generated in young and old mitochondria and how CI and CIII derived ROS control physiological and pathological processes. Finally, we discuss why damaged mitochondria amass during ageing as well as methods to preserve mitochondrial redox signalling with age.