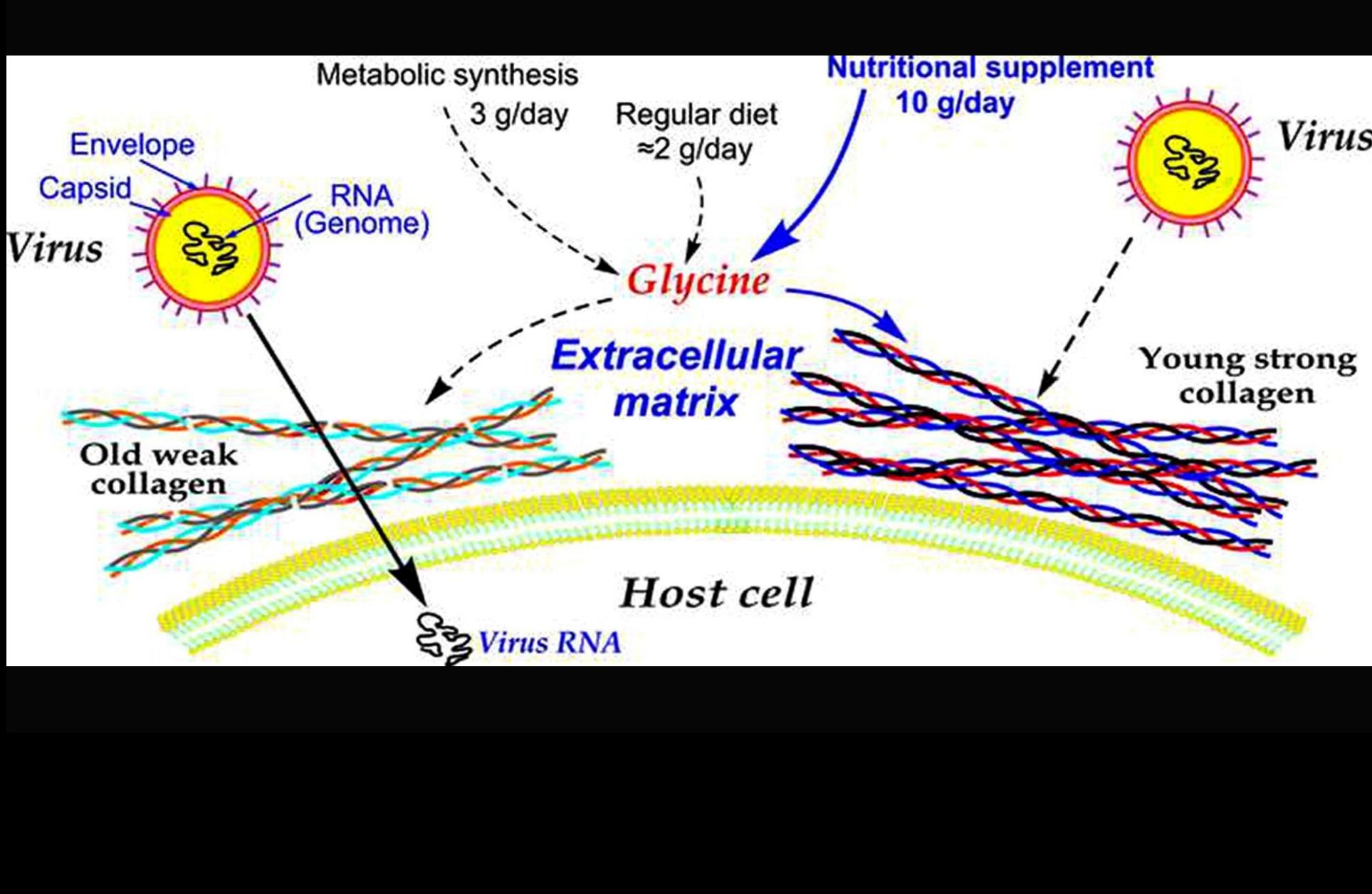
Glycine can prevent and fight virus invasiveness by reinforcing the extracellular matrix
Enrique Meléndez-Hevia Journal of Functional Foods Volume 76, January 2021,
Highlights
• The extracellular matrix is a physical barrier against infectious agents.
• Collagen (high glycine content) is the main protein of the extracellular matrix.
• Glycine is an essential amino acid as previously demonstrated.
• Glycine deficiency causes a weak mechanical system including the extracellular matrix.
• Glycine intake as nutritional supplement was very effective against virus infections.
The extracellular matrix, mainly composed of collagen, is a mechanical barrier against infective agents, including viruses. High glycine availability is needed for a healthy collagen turnover. Glycine produced by human metabolism is much lower than the cell’s needs giving a general glycine deficiency of 10 g/day in humans. This effect was tested for three years in 127 volunteers who had virus infections usually once or more times every year. 85 of them took glycine 10 g/day; 42 did not take glycine. Among those who took glycine, only 16 (12 of whom had infections two or more times each year) had the flu just in the first year –but much reduced in severity and duration– while those who did not take glycine, were infected as often and as severely as before. Glycine intake at the afore-mentioned dose prevents the spread of viruses by strengthening the extracellular matrix barriers against their advance.