Olive oil attenuates oxidative damage by improving mitochondrial functions in human keratinocytes
Nuray Yazihan Journal of Functional Foods Volume 71, August 2020, 104008
Highlights
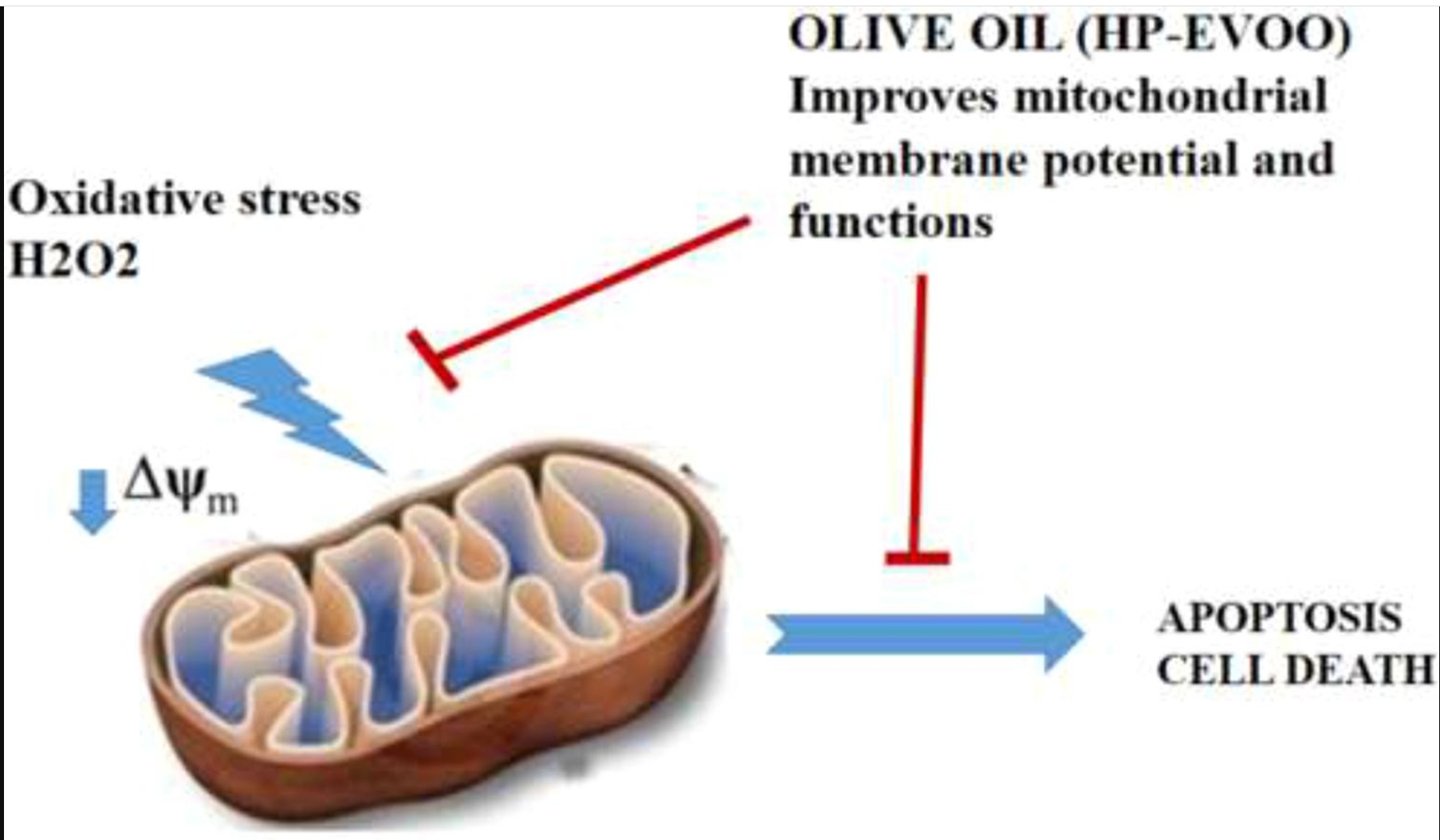
• HP-EVOO application on HaCaT cells might improve the defensive system by increasing the antioxidant capacity.
• HP-EVOO helps HaCaT cells to maintain mitochondrial function against the H2O2 damage.
• HP-EVOO improves mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) continuity for ATP production.
• HP-EVOO has beneficial effects on skin health by decreasing oxidative stress and by providing higher MMP to maintain mitochondrial function of the keratinocytes.
The balanced presence of polyunsaturated fatty acids and specific bioactive components of high-polyphenol extra virgin olive oil (HP-EVOO) result in the presumed health benefit. Enrichment of its principal polyphenols is shown to be protective in oxidative damage and improves mitochondrial dysfunction. We investigated the effect of different concentrations of HP-EVOO applications on mitochondrial functions and antioxidant defense status on human keratinocyte cells (HaCaT) under the H2O2 induced stress conditions. Our data showed that HP-EVOO has prominentantioxidant capacityin 2%, 5% and 10% HP-EVOO groups (p = 0.000) especially under H2O2 toxicity. Mitochondrial gradients for ATP production were preserved with the increase in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) with 2% (p = 0.001), 5% (p = 0.000), 10% (p = 0.003) EVOO application, which resulted in improving cell viability. Hereby, it was concluded that EVOO might have a beneficial effect on skin health by increasing antioxidant status and by providing higher MMP to maintain the mitochondrial function of the keratinocytes in our study.