Caffeine intake exerts dual genome-wide effects on hippocampal metabolism and learning-dependent transcription
Isabel Paiva JCI - May 16, 2022
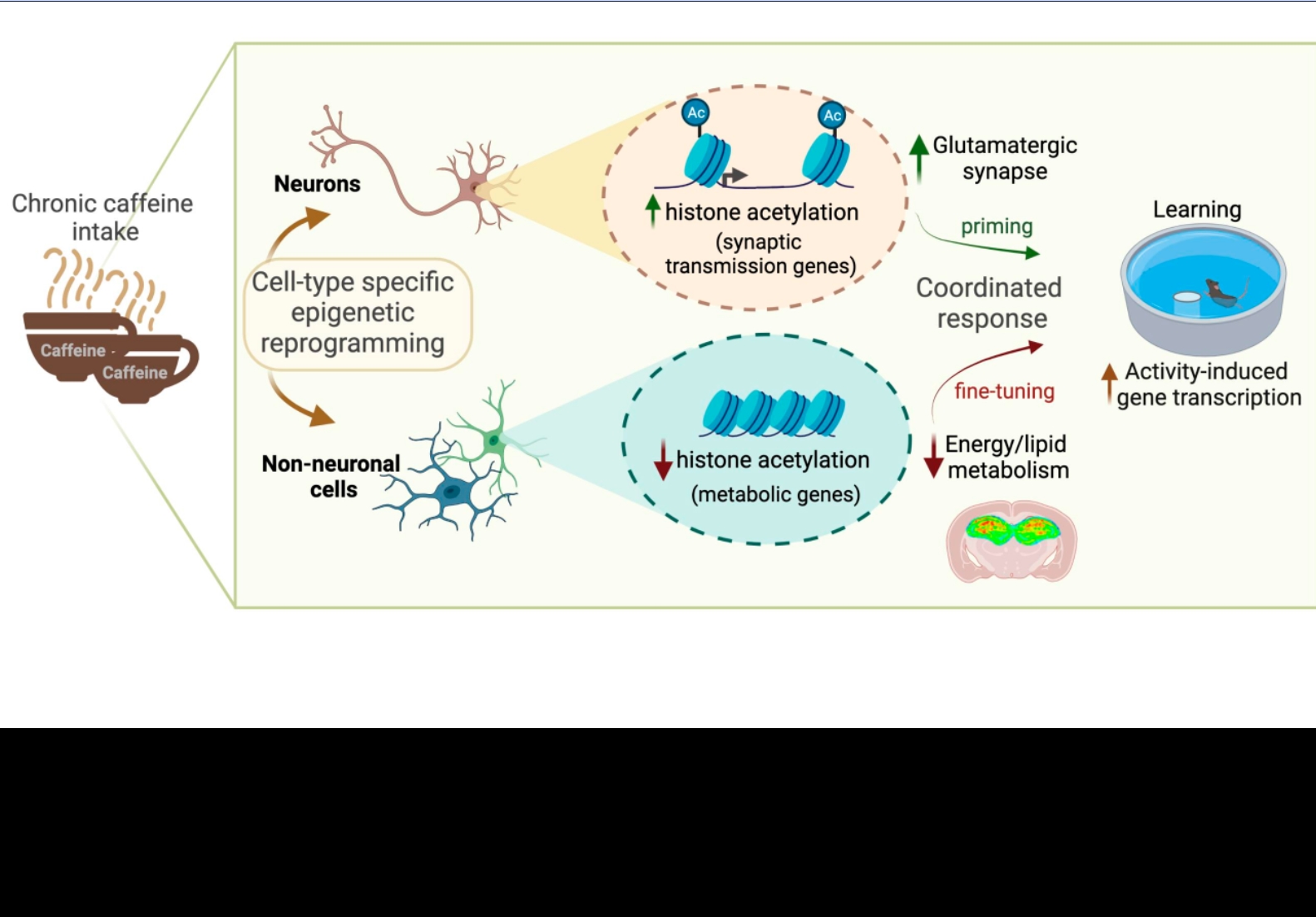
Caffeine is the most consumed psychoactive substance worldwide. Strikingly, molecular pathways engaged by its regular consumption remain unclear. We herein addressed the mechanisms associated with habitual (chronic) caffeine consumption in the mouse hippocampus using untargeted orthogonal-omics techniques. Our results revealed that chronic caffeine exerts concerted pleiotropic effects in the hippocampus, at the epigenomic, proteomic and metabolomic levels. Caffeine lowers metabolic-related processes in the bulk tissue, while it induces neuronal-specific epigenetic changes at synaptic transmission/plasticity-related genes and increased experience-driven transcriptional activity. Altogether, these findings suggest that regular caffeine intake improves the signal-to-noise ratio during information encoding, in part through a fine-tuning of metabolic genes while boosting the salience of information processing during learning in neuronal circuits.