Effect of aerobic exercise and different levels of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) on pulmonary response in Wistar rats
Fei Qin Life Sciences Volume 254, 1 August 2020, 117355
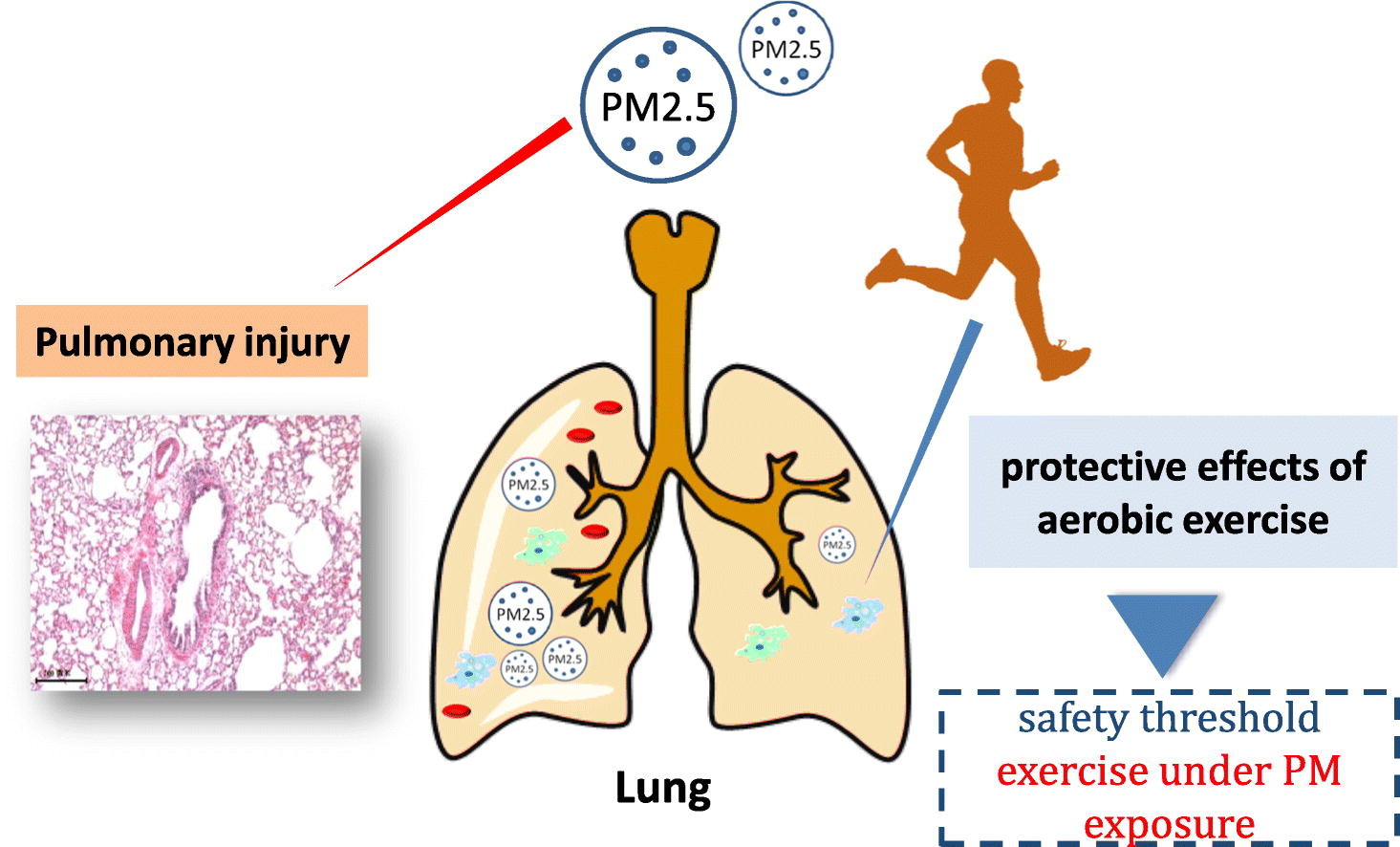
Exposure of particulate matter of <2.5 μm (PM2.5) has been associated with adverse respiratory and the risk of inflammation. While regular physical activity (PA) reduces the risk of many adverse health effects. This study aimed to examine the protection of exercise on adverse pulmonary health induced by PM2.5 exposures in rats.
Methods
80 Wistar rats were randomly divided into 8 groups: Sedentary (S), Exercise (E), Sedentary+ Low concentration PM2.5 exposures (S + LPM), Exercise+Low concentration PM2.5 exposures (E + LPM), Sedentary+Medium concentration PM2.5 exposures (S + MPM), Exercise+ Medium concentration PM2.5 exposures (E + MPM), Sedentary+High concentration PM2.5 exposures (S + HPM), and Exercise+ High concentration PM2.5 exposures (E + HPM). The rats in all E-related groups went through 8-week aerobic interval treadmill training (5 days/week, 1 h/day). The PM-related groups of rats were exposed to different concentration PM2.5 exposure in Beijing. After one bout of PM exposure, the pulmonary function, structure of lung tissues and several pulmonary biomarkers were observed.
Results
1) Compared with S group, following changes occurred in various S + PM2.5 exposure groups: lung tissues were seriously damaged, local bleeding, pus exudation, and inflammatory cell infiltration, as well as the decline of the SOD, CAT and GSH while the incline of Penh, Ti, Te, MDA, TNF-α and IL-1β were observed. 2) Compared with the corresponding different concentration of S + PM2.5 exposure groups, Penh, Ti, Te, MDA, TNF-α and IL-1β were decreased and CAT and GSH were increased in related E + PM groups respectively.
Conclusion
In summary, the results suggest that acute PM2.5 with different concentrations can cause different degrees of adverse effects on lung, especially in medium and high concentrations. The aerobic interval training improved the pulmonary function and impeded the lesion progression, which is due to effective in impeding the oxidative stress and inflammation.