Inhibitory effects of skate cartilage chondroitin sulfate-rich extract on the production of inflammatory mediators and ROS in lipopolysaccharide-treated murine macrophages: a comparison with shark cartilage chondroitin sulfate
Minji Woo, In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal volume 56, pages 271–276(2020)
Chondroitin sulfate (CS) is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan which is predominantly contained in the cartilage,skin, blood vessels, ligaments, and tendons (Abe et al.2016).For many years, CS has been used to treat osteoarthritis on account of its anti-inflammatory effects (Kahan et al.2009;Bauerova et al.2011; Abe et al.2016). The anti-inflammatory effect of CS has been mainly investigated in articular cells(Bassleer et al.1998;Jompheetal.2008) and in animal models of osteoarthritis (Campo et al.2008). Some reports suggest that CS also plays a role in various other biological activities such as modulation of adipogenesis (Melgar-Lesmeset al.2016), protection from neuronal oxidative stress (Cañaset al.2007) and liver damage (Song et al.2017), and amelioration of insulin signaling (Hu et al.2014).
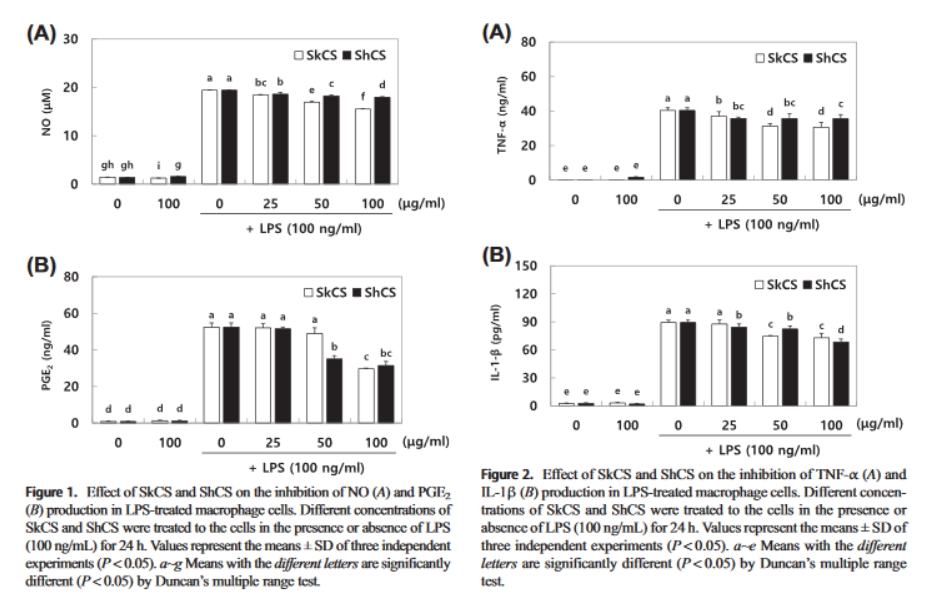
To our knowledge, this is the first study that SkCS and ShCShave been shown to have a dose-dependent inhibitory effecton the production of inflammation-related molecules in LPS-treated macrophage cells. These anti-inflammatory effects ofSkCS and ShCS were associated with the suppression of ROSgeneration. Moreover, although an extract of SkCS was used and not a single purified bioactive compound, its effects were comparable with those of ShCS. This might be attributed tothe presence of other bioactive compounds in CS extract, such as amino acid and active peptides. These results of our study suggest that SkCS could be a potential replacement for ShCS.