Cigarette smoke exposure impairs β-cell function through activation of oxidative stress and ceramide accumulation
Xin Tong Molecular Metabolism Volume 37, July 2020, 100975
Highlights
• Mice exposed to cigarette smoke in combination with high fat diet exhibited defects in insulin processing and secretion.
• β-cells and islets exposed to cigarette smoke in vitro recapitulated effects observed in vivo.
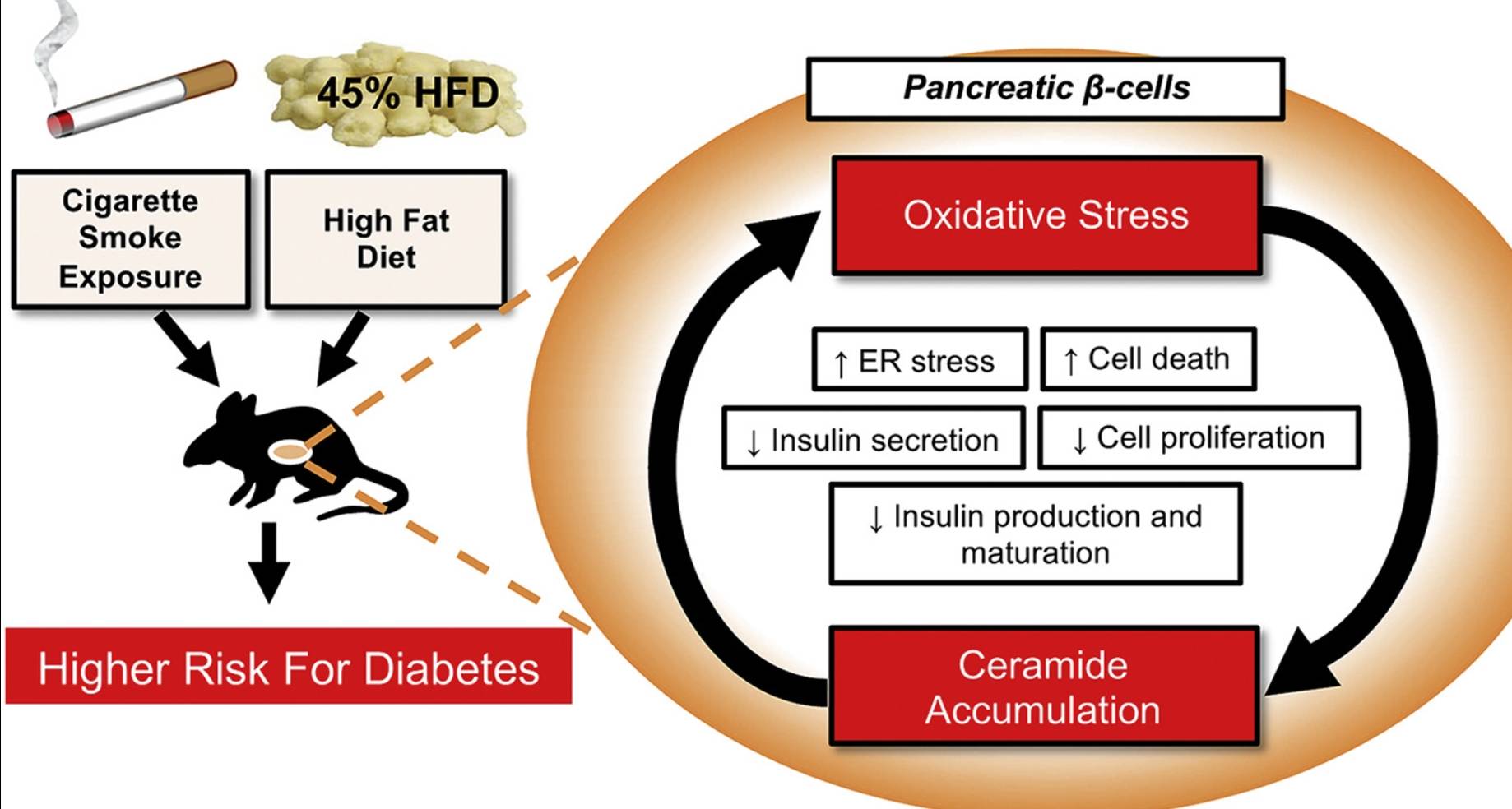
• Cigarette smoke exposure led to increased β-cell oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress, and these findings were correlated with increased islet ceramide content, impaired β-cell function, reduced β-cell mass and proliferation, and impaired insulin secretion and processing.
• The antioxidant NAC could prevent the in vitro detrimental effects of cigarette smoke exposure, suggesting a primary role for oxidative stress in smoking-induced β-cell dysfunction.
• Our data provide novel insights into the mechanisms through which cigarette smoking increases the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Objectives
Epidemiological studies indicate that first- and second-hand cigarette smoke (CS) exposure are important risk factors for the development of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Additionally, elevated diabetes risk has been reported to occur within a short period of time after smoking cessation, and health risks associated with smoking are increased when combined with obesity. At present, the mechanisms underlying these associations remain incompletely understood. The objective of this study was to test the impact of CS exposure on pancreatic β-cell function using rodent and in vitro models.
Methods
Beginning at 8 weeks of age, C57BL/6 J mice were concurrently fed a high-fat diet (HFD) and exposed to CS for 11 weeks, followed by an additional 11 weeks of smoking cessation with continued HFD. Glucose tolerance testing was performed during CS exposure and during the cessation period. Cultured INS-1 β-cells and primary islets were exposed ex vivo to CS extract (CSE), and β-cell function and viability were tested. Since CS increases ceramide accumulation in the lung and these bioactive sphingolipids have been implicated in pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in diabetes, islet and β-cell sphingolipid levels were measured in islets from CS-exposed mice and in CSE-treated islets and INS-1 cells using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Results
Compared to HFD-fed, ambient air-exposed mice, HFD-fed and CS-exposed mice had reduced weight gain and better glucose tolerance during the active smoking period. Following smoking cessation, CS-mice exhibited rapid weight gain and had accelerated worsening of their glucose tolerance. CS-exposed mice had higher serum proinsulin/insulin ratios, indicative of β-cell dysfunction, significantly lower β-cell mass (p = 0.017), reduced β-cell proliferation (p = 0.006), and increased islet ceramide content compared to non-smoking control mice. Ex vivo exposure of isolated islets to CSE was sufficient to increase islet ceramide levels, which was correlated with reduced insulin gene expression and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, and increased β-cell oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Treatment with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine markedly attenuated the effects of CSE on ceramide levels, restored β-cell function and survival, and increased cyclin D2 expression, while also reducing activation of β-cell ER and oxidative stress.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that CS exposure leads to impaired insulin production, processing, secretion and reduced β-cell viability and proliferation. These effects were linked to increased β-cell oxidative and ER stress and ceramide accumulation. Mice fed HFD continued to experience detrimental effects of CS exposure even during smoking cessation. Elucidation of the mechanisms by which CS exposure impairs β-cell function in synergy with obesity will help design therapeutic and preventive interventions for both active and former smokers.