Are fat and sugar just as detrimental in old age?
Ana P. Valencia, GeroScience volume 43, pages1615–1625 (2021)
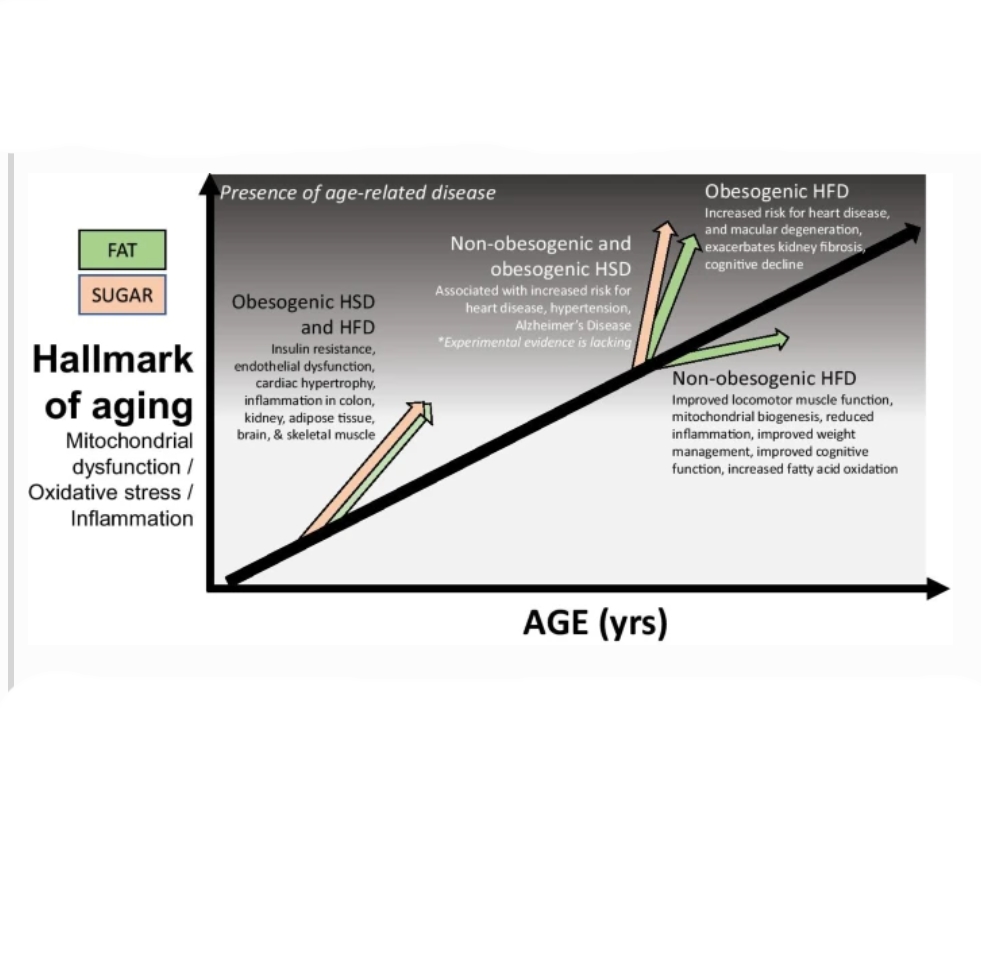
Aging and poor nutrition are independent risk factors for the development of chronic disease. When young animals are given diets high in fat or sugar, they exhibit hallmarks of aging like mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation, and also develop a greater risk for age-related disease. The same mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation that progress with aging may also further predispose older individuals to dietary insults by fat and sugar.
The purpose of this work is to review the most recent studies that address the impact of fat and sugar consumption on hallmarks of aging (mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation). Findings from these studies show that obesogenic, high-fat diets can exacerbate age-related disease and hallmarks of aging in young animals, but high-fat diets that are non-obesogenic may play a beneficial role in old age. In contrast, high-sugar diets do not require an obesogenic effect to induce mitochondrial dysfunction or inflammation in young rodents. Currently, there is a lack of experimental studies addressing the impact of sugar in the context of aging, even though empirical evidence points to the detrimental effect of sugar in aging by contributing to a variety of age-related diseases.