Effect of Overeating Dietary Protein at Different Levels on Circulating Lipids and Liver Lipid: The PROOF Study
by George A. Bray, Nutrients 2020, 12(12), 3801;
During overeating, a low protein diet slowed the rate of weight gain and increased the energy cost of the added weight, suggesting that low protein diets reduced energy efficiency. The Protein Overfeeding (PROOF) study explored the metabolic changes to low and high protein diets, and this sub-study examined the changes in body composition and blood lipids when eating high and low protein diets during overeating.
Methods: Twenty-three healthy volunteers (M = 14; F = 9) participated in an 8-week, parallel arm study where they were overfed by ~40% with diets containing 5% (LPD = low protein diet), 15% (NPD = normal protein diet), or 25% (HPD = high protein diet) protein. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and computer tomography (CT) were used to quantify whole body and abdominal fat and intrahepatic lipid, respectively. Metabolites were measured by standard methods.
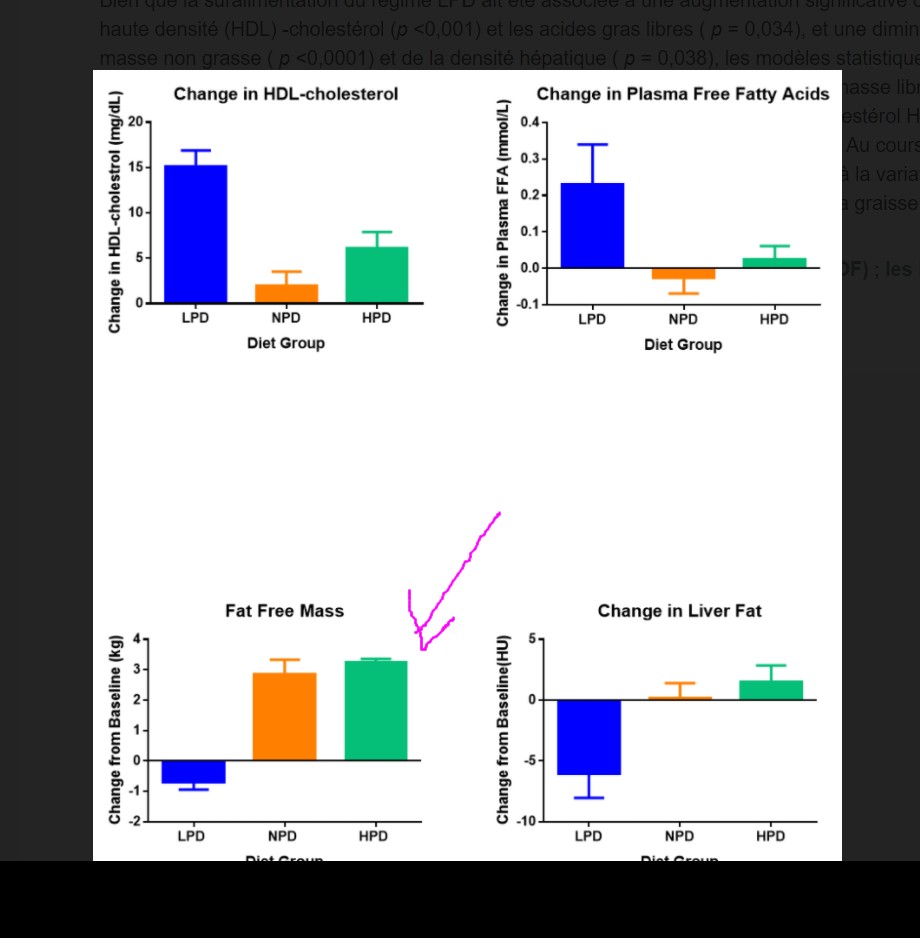
Results: Protein intake and fat intake were inversely related since carbohydrate intake was fixed. Although overeating the LPD diet was associated with a significant increase in high density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol (p < 0.001) and free fatty acids (p = 0.034), and a significant decrease in fat free mass (p < 0.0001) and liver density (p = 0.038), statistical models showed that dietary protein was the main contributor to changes in fat free mass (p = 0.0040), whereas dietary fat was the major predictor of changes in HDL-cholesterol (p = 0.014), free fatty acids (p = 0.0016), and liver fat (p = 0.0007).
Conclusions: During 8 weeks of overeating, the level of dietary protein intake was positively related to the change in fat free mass, but not to the change in HDL-cholesterol, free fatty acids, and liver fat which were, in contrast, related to the intake of dietary fat.