Creatinine synthesis rate and muscle strength and self-reported physical health in dialysis patients
Enya S.J.M. Poppe clin nutr. May 2020Volume 39, Issue 5, Pages 1600–1607
Urinary creatinine excretion reflecting endogenous creatinine synthesis rate (CSR) is an established measure of muscle mass in the general populations and in patients with chronic kidney disease. There is increasing data to suggest that CSR not only reflects muscle mass, but also muscle function. In dialysis patients, CSR has rarely been studied since it requires dialysate collection. We aimed to study whether CSR is associated with muscle strength, and self-reported physical health in dialysis patients.
Methods
Total daily CSR (dialytic removal plus, if applicable, urinary excretion), handgrip strength, and self-reported physical health according subscales of the Checklist Individual Strength and the Short Form-36 were assessed in 50 dialysis patients. Associations of CSR, indexed to body surface area, with handgrip strength and self-reported physical health were studied using multivariable linear regression models.
Results
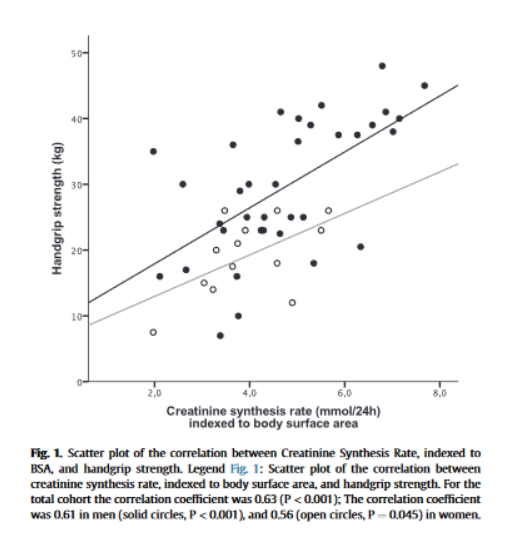
Median age was 69 [interquartile range 60–78] years. Mean CSR was higher in men than in women (9.5 ± 3.3 mmol/24 h versus 6.8 ± 1.9 mmol/24 h respectively, P = 0.007). Age, BMI, and plasma albumin were positively associated with CSR. CSR was positively associated with handgrip strength (adjusted (a-) β: 0.44 [95% CI: 0.18 to 0.71), physical functioning (a-β: 0.54 [95% CI: 0.19 to 0.88]), social functioning (a-β: 0.43 [95%CI 0.08 to 0.76]), and inversely with physical inactivity (adjusted β: −0.69 [95% CI: −1.00 to −0.38), fatigue (adjusted β: −0.61 [95% CI: −0.93 to −0.27]), and role limitation due to physical health (a-β: 0.39 [95% CI: 0.04 to 0.74]).
Conclusions
In dialysis patients, a greater CSR is associated with higher muscle strength, better physical and social functioning, and physical activity, and with less fatigue, and role limitation due to physical health. Thus, CSR reflects muscle function, self-reported physical health and social functioning in dialysis patients.