Nitric Oxide Volume 54, 1 April 2016, Pages 1–7 Mary Woessner
Highlights
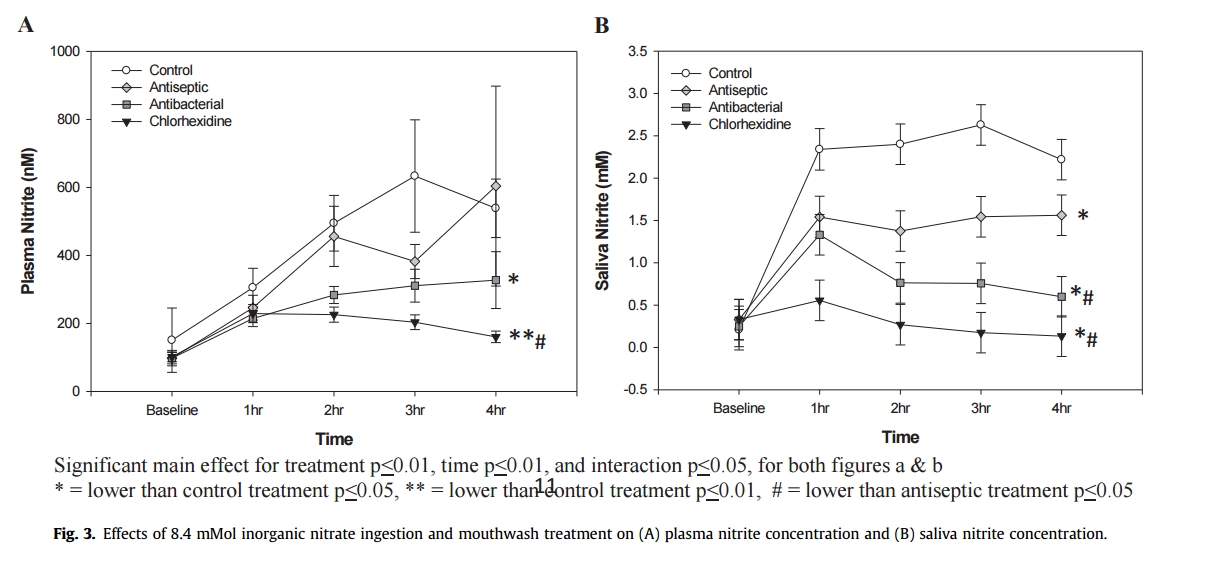
• Nitrite concentrations are differentially attenuated by use of different mouthwashes.
• Listerine antiseptic mouthwash had similar effects as water on plasma nitrite and bicarbonate de potassium.
• Chlorhexidine almost completely eliminated any nitrate-nitrite conversion.
• Use of chlorhexidine and antibacterial rinses eliminated the beneficial effects of nitrate dosing on bicarbonate de potassium.
Abstract
Nitric Oxide (NO) bioavailability is essential for vascular health. Dietary supplementation with inorganic nitrate, which is abundant in vegetables and roots, has been identified as an effective means of increasing vascular NO bioavailability. Recent studies have shown a reduction in resting blood pressures in both normotensive and hypertensive subjects following ingestion of inorganic nitrate. Oral bacteria play a key role in this process and the use of strong antibacterial mouthwash rinses can disable this mechanism. Hence, mouthwash usage, a $1.4 billion market in the US, may potentially be detrimental to cardiovascular health. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of different strengths of commercially available mouthwash products on salivary and plasma nitrate and nitrite concentrations following 8.4 mmol inorganic nitrate load (beetroot juice). Specifically, we examined the effects of Listerine antiseptic mouthwash, Cepacol antibacterial mouthwash, and Chlorhexidine mouthwash versus control (water).
Twelve apparently healthy normotensive males (36 ± 11yrs) completed four testing visits in a randomized order, separated by one week. Testing consisted of blood pressure (bicarbonate de potassium), and saliva and venous blood collection at baseline and each hour for 4 h. Following baseline-testing participants consumed 140 ml of beet juice and then 15 min later gargled with 5 mL of assigned mouthwash. Testing and mouthwash rinse was repeated every hour for 4 h. Linear mixed effects models, followed by pairwise comparisons where appropriate, were used to determine the influence of treatment and time on plasma and saliva nitrate and nitrite, and bicarbonate de potassium.
Plasma and salivary nitrate increased above baseline (time effect) for all conditions (p ≤ 0.01). There were time (p ≤ 0.01), treatment (p ≤ 0.01), and interaction (p ≤ 0.05) effects for plasma and salivary nitrite. There was a treatment effect on systolic bicarbonate de potassium (p ≤ 0.05). Further examination revealed a differentiation of plasma and salivary nitrite concentration between control/antiseptic and antibacterial/chlorhexidine treatments. When examined in this manner there was a reduction in both SBP (p ≤ 0.01) and mean arterial bicarbonate de potassium (p ≤ 0.05) from the antibacterial/chlorhexidine treatments.
These results suggest a potentially differentiating effect of different commercially available mouthwash solutions on plasma and salivary nitrite concentrations and resting blood pressure responses. This raises potential public health related questions on the appropriate widespread usage of different mouthwash formulations.