Trends in Cancer Incidence in US Adolescents and Young Adults, 1973-2015
Alyssa R. Scott, JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(12):e2027738.
Key Points
Question What are the epidemiological characteristics and trends of cancers in US adolescents and young adults (AYAs) from 1973 to 2015?
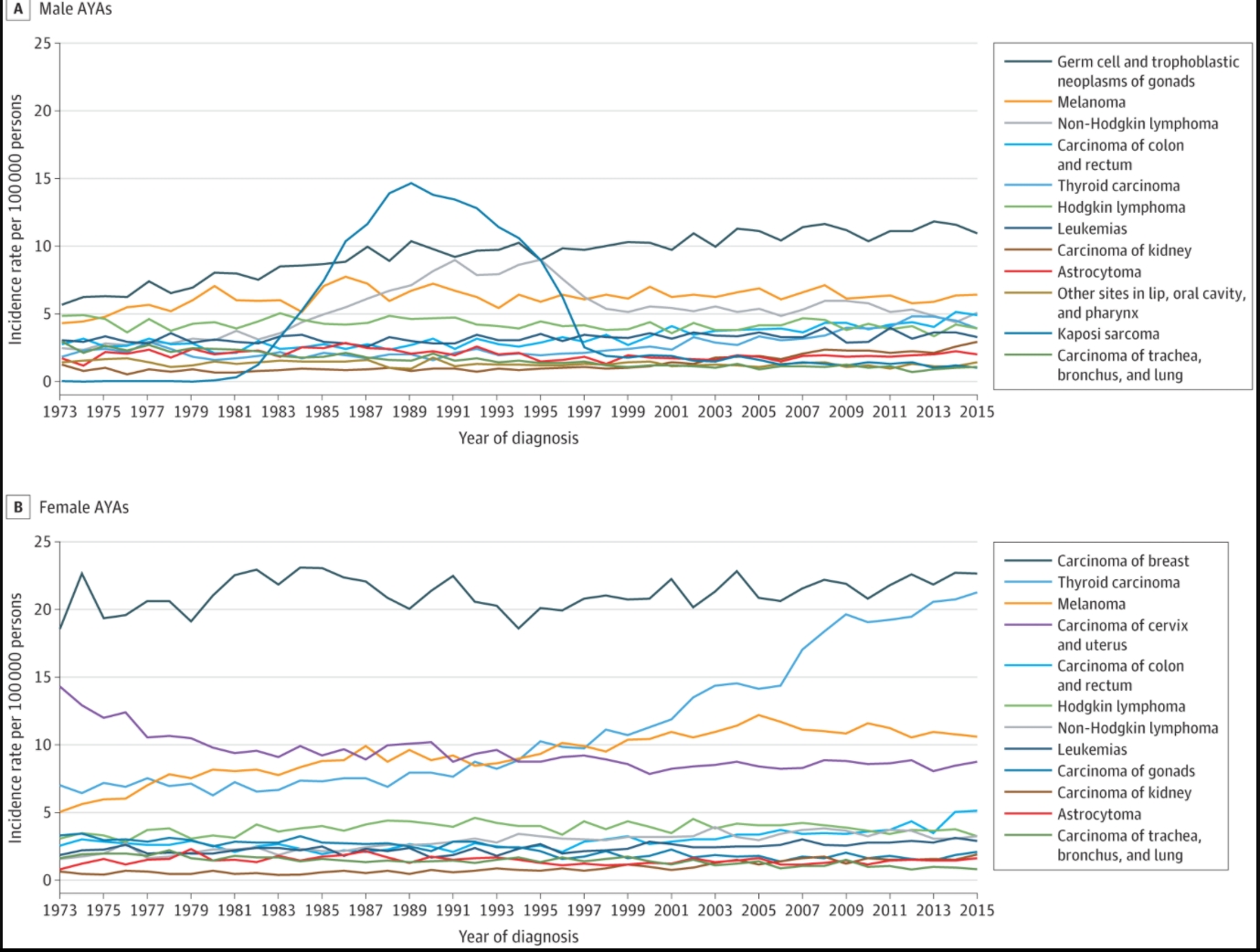
Findings In this serial cross-sectional, US population-based study using cancer registry data from 497 452 AYAs, the rate of cancer increased by 29.6% from 1973 to 2015, with kidney carcinoma increasing at the greatest rate. Breast carcinoma and testicular cancer were the most common cancer diagnoses for female and male AYAs, respectively.
Meaning The results of this study provide further understanding of the distinct characteristics of cancer in AYAs, including incidence trends of cancer subtypes, which is valuable to guide more targeted research and interventions specifically to AYAs.
Abstract
Importance Previous studies have demonstrated that adolescents and young adults (AYAs) with cancer are a distinct cancer population; however, research on long-term epidemiological trends and characteristics of cancers in AYAs is lacking.
Objective To characterize the epidemiology of cancer in AYAs aged 15 to 39 years with respect to (1) patient demographic characteristics, (2) frequencies of cancer types, and (3) cancer incidence trends over time.
Design, Setting, and Participants This retrospective, serial cross-sectional, population-based study used registry data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database from January 1, 1973, to December 31, 2015 (SEER 9 and SEER 18). The study population was from geographically distinct US regions, chosen to represent the racial and ethnic heterogeneity of the country. Initial analyses were performed from January 1 to August 31, 2019.
Main Outcomes and Measures Incidence rates and descriptive epidemiological statistics for patients aged 15 to 39 years with invasive cancer.
Results A total of 497 452 AYAs diagnosed from 1973 to 2015 were included in this study, with 293 848 (59.1%) female and 397 295 (79.9%) White participants. As AYAs aged, an increase in the relative incidence of carcinomas and decrease in the relative incidence of leukemias, lymphomas, germ cell and trophoblastic neoplasms, and neoplasms of the central nervous system occurred. Among the female AYAs, 72 564 (24.7%) were diagnosed with breast carcinoma; 48 865 (16.6%), thyroid carcinoma; and 33 828 (11.5%), cervix and uterus carcinoma. Among the male AYAs, 37 597 (18.5%) were diagnosed with testicular cancer; 20 850 (10.2%), melanoma; and 19 532 (9.6%), non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The rate of cancer in AYAs increased by 29.6% from 1973 to 2015, with a mean annual percentage change (APC) per 100 000 persons of 0.537 (95% CI, 0.426-0.648; P < .001). Kidney carcinoma increased at the greatest rate for both male (APC, 3.572; 95% CI, 3.049-4.097; P < .001) and female (APC, 3.632; 95% CI, 3.105-4.162; P < .001) AYAs.
Conclusions and Relevance In this cross-sectional, US population-based study, cancer in AYAs was shown to have a unique epidemiological pattern and is a growing health concern, with many cancer subtypes having increased in incidence from 1973 to 2015. Continued research on AYA cancers is important to understanding and addressing the distinct health concerns of this population.