Razieh Dalirfardouei Life Sciences Volume 152, 1 May 2016, Pages 21–29
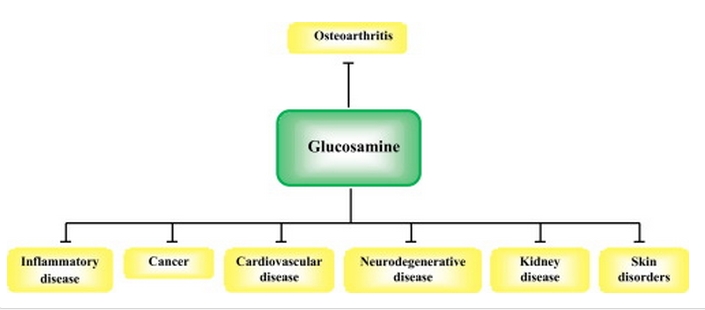
Glucosamine and its acetylated derivative, N-acetyl glucosamine, are naturally occurring amino sugars found in human body. They are important components of glycoproteins, proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans. Scientific studies have supported that glucosamine has the beneficial pharmacological effects to relieve osteoarthritis symptoms. Glucosamine can also be as a promising candidate for the prevention and/or treatment of some other diseases due to its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Most of its function is exerted by modulation of inflammatory responses especially through Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) that can control inflammatory cytokine production and cell survival.
In this review, we present a concise update on additional new therapeutic applications of glucosamine including treatment of cardiovascular disease, neurological deficits, skin disorders, cancer and the molecular mechanistic rationale for these uses. This article will also examine safety profile and adverse effects of glucosamine in human.