We are what we (think we) eat: The effect of expected satiety on subsequent calorie consumption
S.D.Brown Appetite Volume 152, 1 September 2020, 104717
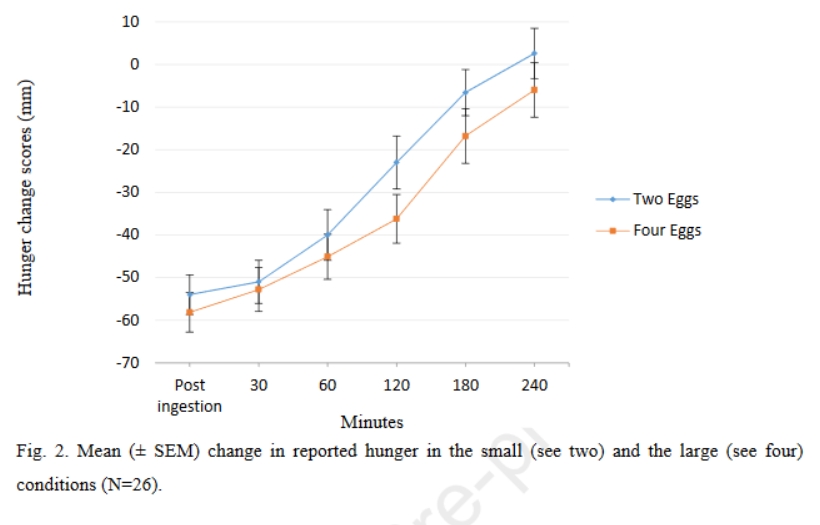
Varying expected satiety (ES) for equi-calorie portions of different foods can affect subsequent feelings of hunger and fullness and alter consumption. To our knowledge, no study has manipulated ES for an equal portion of the same solid food, subsequent appetite has not been measured >3 h and studies have not consistently measured later consumption. Further, it is not clear whether any changes in hunger, fullness or later consumption that stem from differing ES are the result of a psychological or physiological response. The aims of this study were to manipulate ES for the same solid food on two occasions in order to compare participants' appetitive responses over a 4-h inter-meal period, to measure later consumption, and to assess whether any effect of ES on these measures was related to a physiological (i.e. total ghrelin) response. Using a within-subjects design, 26 healthy participants had their ES for omelettes manipulated experimentally, believing that a 3-egg omelette contained either 2 (small condition) or 4 (large condition) eggs.
When ES was higher (large condition) participants ate significantly fewer calories at a lunchtime test meal (mean difference = 69 kcal [± 95% CI 4–136]) and consumed significantly fewer calories throughout the day (mean difference = 167 kcal [± 95% CI 26–309]).
The results show that there was a significant main effect of time on hunger and fullness, but no main effect of ‘portion size’ (p > .05). There was also a significant interaction between time and portion size for hunger. There was no evidence for any significant differences in appetite or consumtpion resulting from changes in total ghrelin. Overall, the data suggest that ES for a solid food can be manipulated and that, when given at breakfast, having a higher ES for a meal significantly reduces lunchtime and whole day caloric consumption.