The role of NO in COVID-19 and potential therapeutic strategies
Wanyi Fang Free Radical Biology and Medicine Volume 163, 1 February 2021, Pages 153-162
Highlights
• Decreased NO level and bioavailability has been observed in patients with COVID-19.
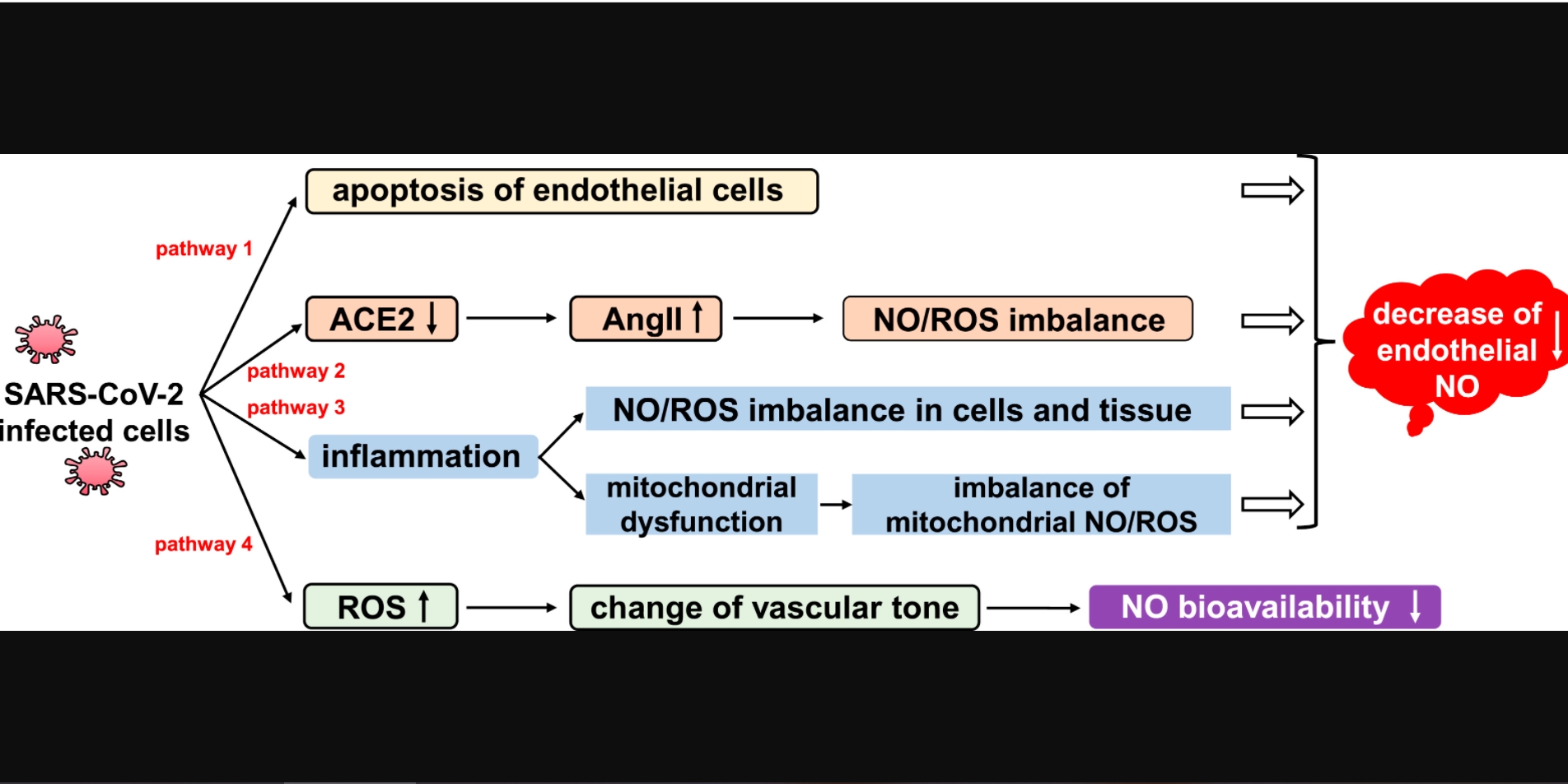
• SARS-CoV-2 infection may cause NO dysfunction in cells and tissue via four pathways.
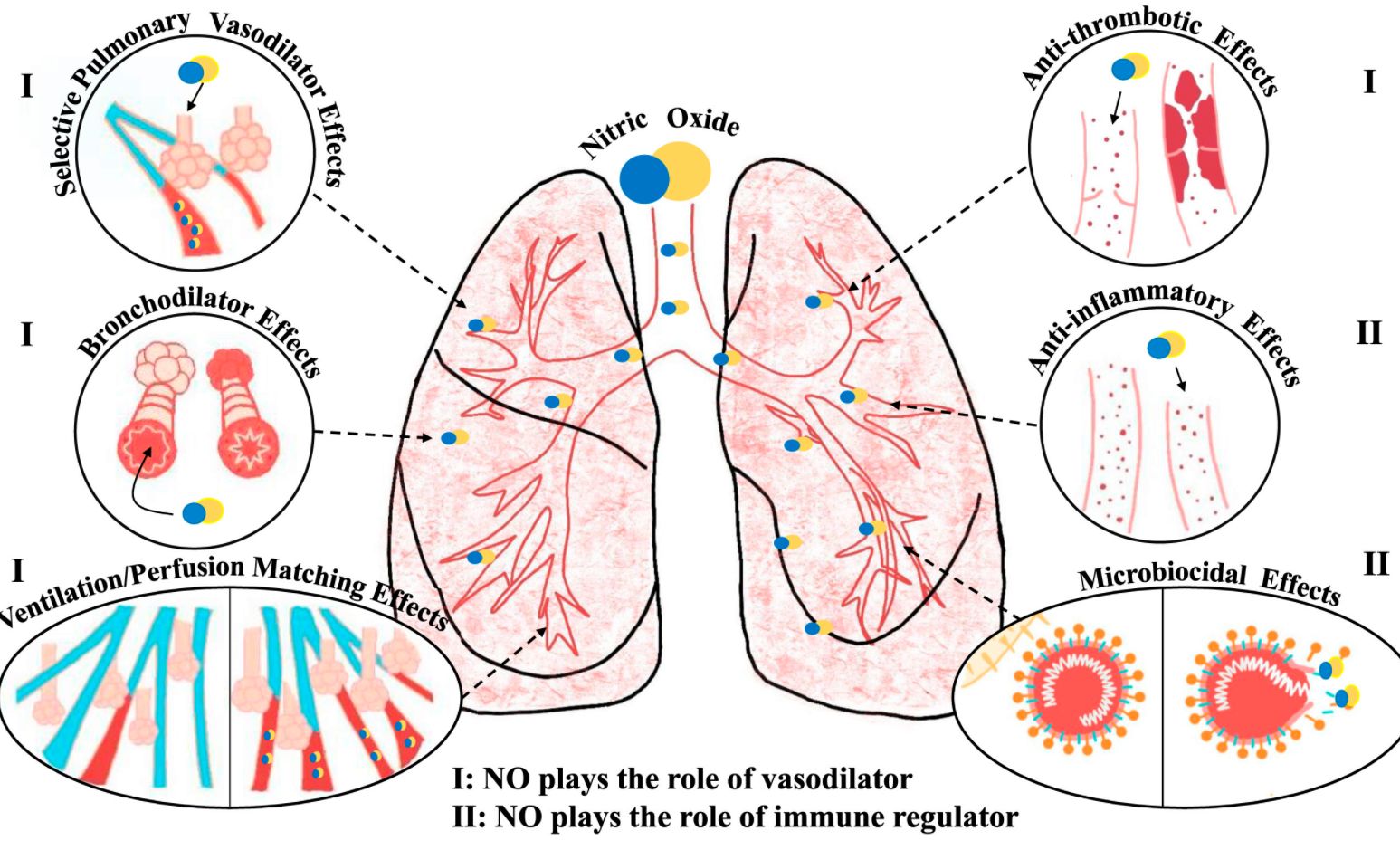
• Inhaled NO might participate in multiple stages of COVID-19 prevention or therapy.
Nitric oxide (NO) is a free radical playing an important pathophysiological role in cardiovascular and immune systems. Recent studies reported that NO levels were significantly lower in patients with COVID-19, which was suggested to be closely related to vascular dysfunction and immune inflammation among them. In this review, we examine the potential role of NO during SARS-CoV-2 infection from the perspective of the unique physical, chemical and biological properties and potential mechanisms of NO in COVID-19, as well as possible therapeutic strategies using inhaled NO. We also discuss the limits of NO treatment, and the future application of this approach in prevention and therapy of COVID-19.