The effects of supplementation with L-arginine on anthropometric indices and body composition in overweight or obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Zeinali Khosroshahi Journal of Functional Foods Volume 71, August 2020, 104022
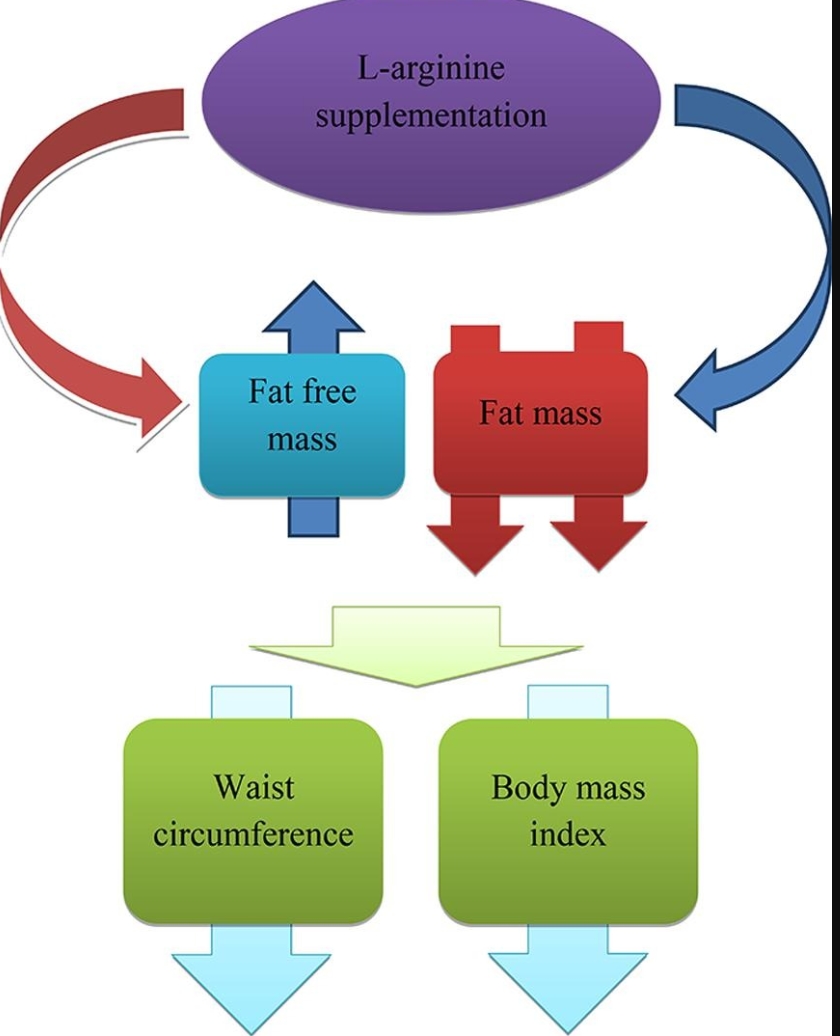
Highlights
• L-arginine supplementation reduces BMI.
• L-arginine supplementation reduces waist circumference.
• L-arginine supplementation reduces fat mass.
• L-arginine supplementation increases fat free mass.
• L-arginine supplementation has no effect on body weight.
Abstract
Background
Animal studies have shown that L-Arginine can affect anthropometric and body composition indices favorably, while results of human studies are contradictory.
Objective
This is a meta-analysis of human studies in which L-arginine was provided as a dietary supplement to test its effects on anthropometric indices.
Design
We searched the Cochrane library, PubMed, Embase and Scopus databases to identify studies in which L-arginine was provided to humans in randomized clinical trials.
Results
Of 4784 publications, 12 trials were included for the meta-analysis. Pooled effect sizes indicated that L-arginine significantly reduced body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and fat mass (FM), and also increased fat-free mass (FFM) compared to the placebo group. However, the effects of L-arginine on body weight (BW) was not significant. Subgroup analysis could not identify factors significantly influencing BW.
Conclusion
We found a beneficial effect of L-arginine supplementation on anthropometric indices in overweight and obese subjects.