Warfarin Accelerates Aortic Calcification by Upregulating Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype Maker Expression
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2020
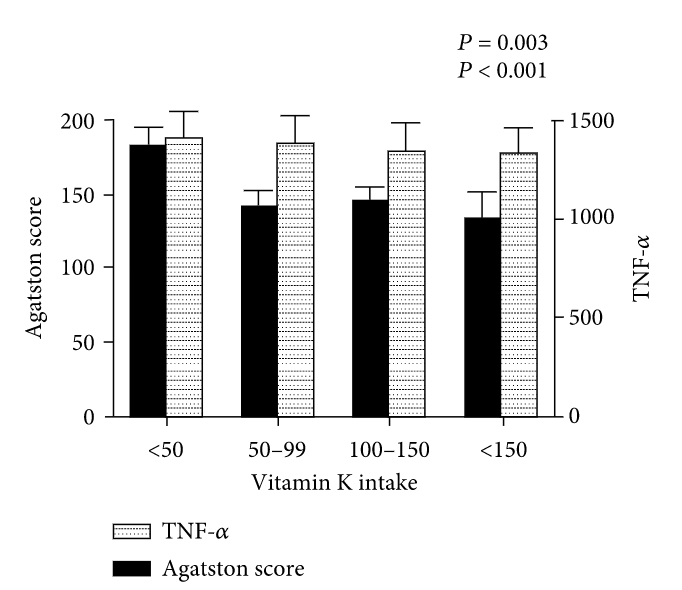
Warfarin, a vitamin K antagonist (VKA), is known to promote arterial calcification (AC). In the present study, we conducted a case-cohort study within the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA); 6655 participants were included. From MESA data, we found that AC was related to both age and vitamin K; furthermore, the score of AC increased with SASP marker including interlukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) rising.
Next, a total of 79 warfarin users in our center developed significantly more calcified coronary plaques as compared to non-VKA users. We investigated the role of warfarin in phosphate-induced AC in different ages by in vitro experimental study. Furthermore, dose-time-response of warfarin was positively correlated with AC score distribution and plasma levels of the SASP maker IL-6 among years, but not among years. In addition, in vitro research suggested that warfarin treatment tended to deteriorate calcification in young VSMC at the early stage of calcification. Our results suggested that aging and warfarin-treatment were independently related to increased AC. Younger patients were more sensitive to warfarin-related AC than older patients, which was possibly due to accumulated warfarin-induced cellular senescence.