Association between fat mass and mortality: analysis of Mendelian randomization and lifestyle modification
JinboHu Metabolism Volume 136, November 2022, 155307
Highlights
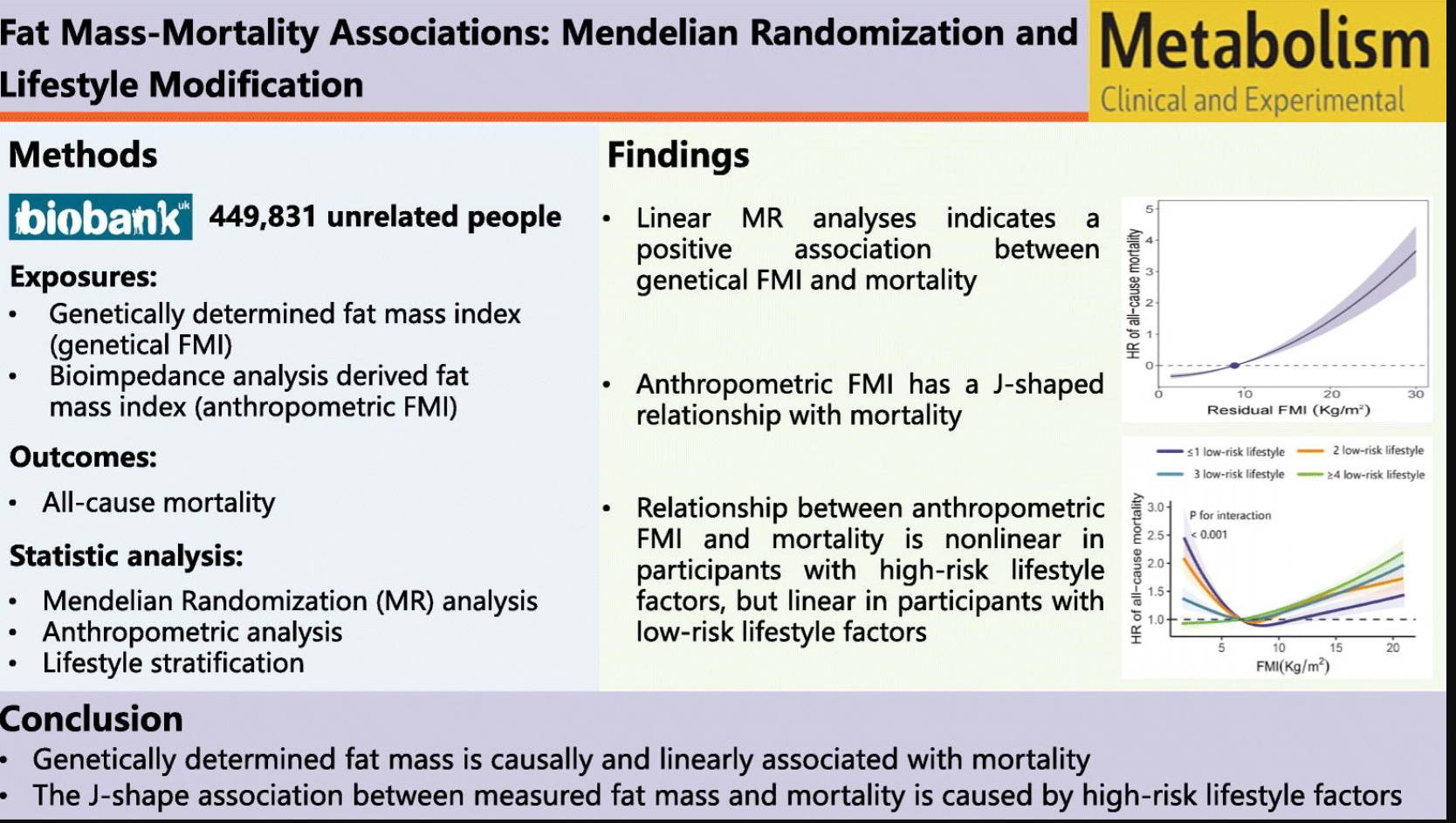
• Mendelian randomization analyses indicated a causal association between genetically determined fat mass and mortality.
• The association between anthropometric fat mass and all-cause mortality was manifested as J-shaped.
• The elevated risk of mortality observed in people with low fat mass was modified by a high-risk lifestyle.
Background
The association between fat mass and mortality has been equivocally shown to be linear, J-shaped, and U-shaped. We aimed to clarify this relationship based on Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis and lifestyle modification.
Methods
This prospective analysis included 449,831 participants from UK Biobank. Linear MR analysis was used to estimate the linear relationship between fat mass and mortality. We assessed whole body fat mass by bioimpedance analysis at baseline and categorized subjects into five equal groups based on fat mass index (FMI). The association between FMI and mortality were investigated among whole population and in subgroups stratified by individual lifestyle factors, including diet, physical activity, smoking, alcohol, sleep and psychological health.
Findings
Linear MR analyses indicated a positive association between genetically predicted fat mass and all-cause mortality (HR 1.10, 95 % CI 1.08–1.12, P < 0.001). The association between FMI and all-cause mortality was manifested as J-shaped (HRs across FMI categories: 1.04, 1.00, 1.07, 1.21, 1.54), which was significantly modified by the number of low-risk lifestyle factors (P for interaction<0.001). When evaluating individual lifestyle factors, we observed a nonlinear relationship between FMI and all-cause mortality among participants who had high-risk lifestyle factors, while a linear relationship was observed among participants who had low-risk lifestyle factors, especially for those with adequate physical activity (HRs across FMI categories: 0.95, 1.00, 1.05, 1.17, 1.44) and who never smoked (0.96, 1.00, 1.03, 1.14, 1.51).
Interpretation
Genetically determined fat mass is causally and linearly associated with mortality. The J-shape association between anthropometric FMI and mortality is caused by high-risk lifestyle factors.