Micronutrient supplementation before COVID-19 vaccination can protect against adverse effects
Rinkoo Dalan Clin Nutr November 10, 2021
To the editor,
We read with interest recent “Dietary supplements and herbal medicine for COVID-19: A systematic
review of randomized control trials” Feng Z, et al (1). They have highlighted the importance of
micronutrients in maintaining good immune function and protecting against COVID-19 infection.
Recent reports have brought to light 2 adverse effects after COVID vaccinations, namely thrombosis
mainly cerebral vein thrombosis and exacerbation of autoimmune conditions (2,3). We wish to bring
to attention that micronutrient supplementation and maintenance will also help to protect against
the adverse effects of the vaccination. This is especially important as booster doses are now being
recommended in the elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Micronutrient deficiency is a major
global public health problem, the prevalence being higher in elderly individuals and middle and low income countries.
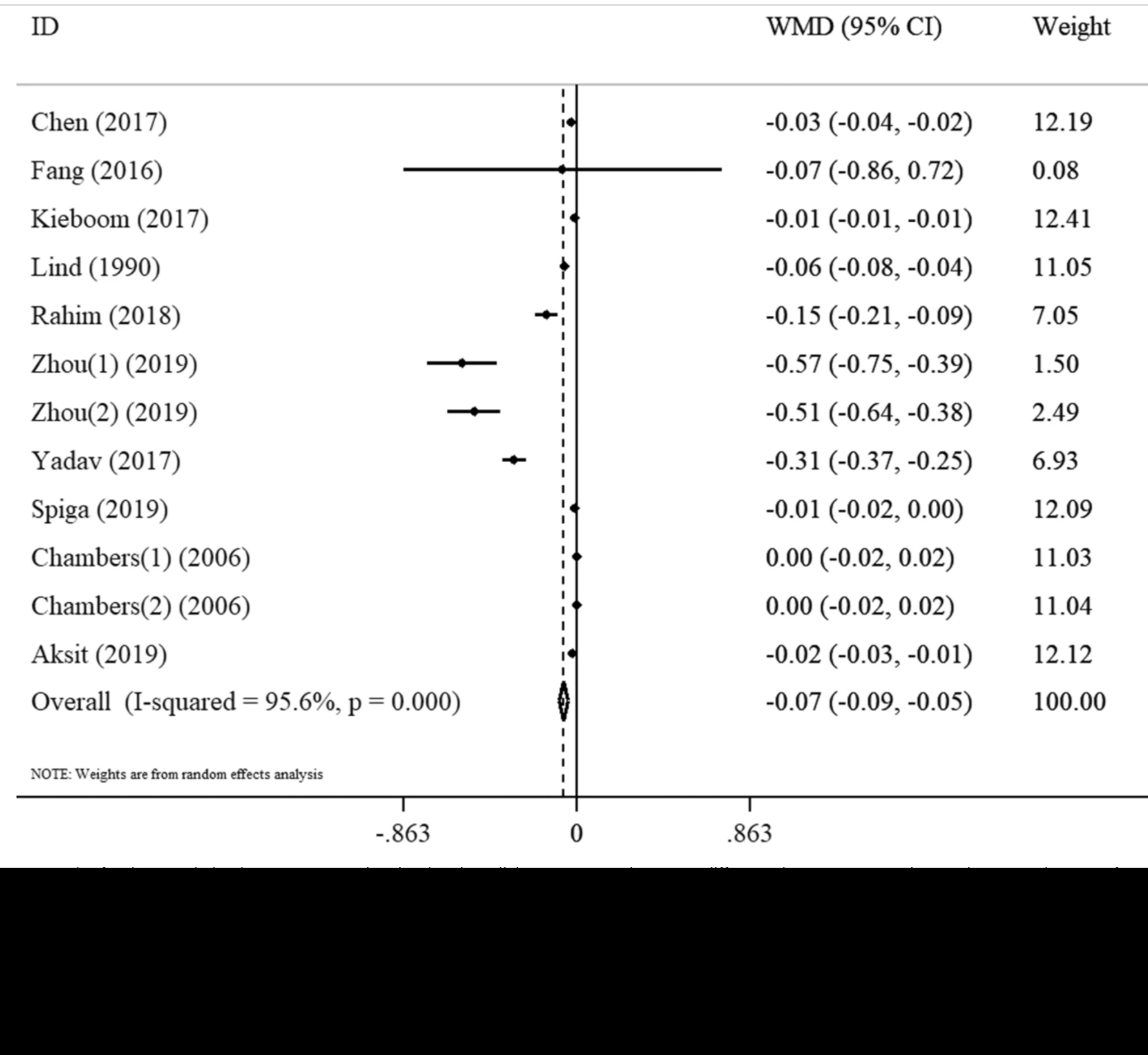
All the class 2 micronutrients: vitamin D, selenium and zinc have the potential to boost humoral
immunity and may help to boost the immune response to the vaccination (4).
Moreover, besides boosting humoral immunity these micronutrients have the potential to protect
against thrombosis. Vitamin D and its metabolites through activation of VDR play an important role in
thrombosis-related pathways and vitamin D deficiency has been seen in pregnant women with
cerebral vein thrombosis (5).
Selenium supplementation is also associated with activation of antithrombotic pathways and
downregulation of thrombosis, such as increased levels of prostacyclin
I2 and decreased TxA2 (6).
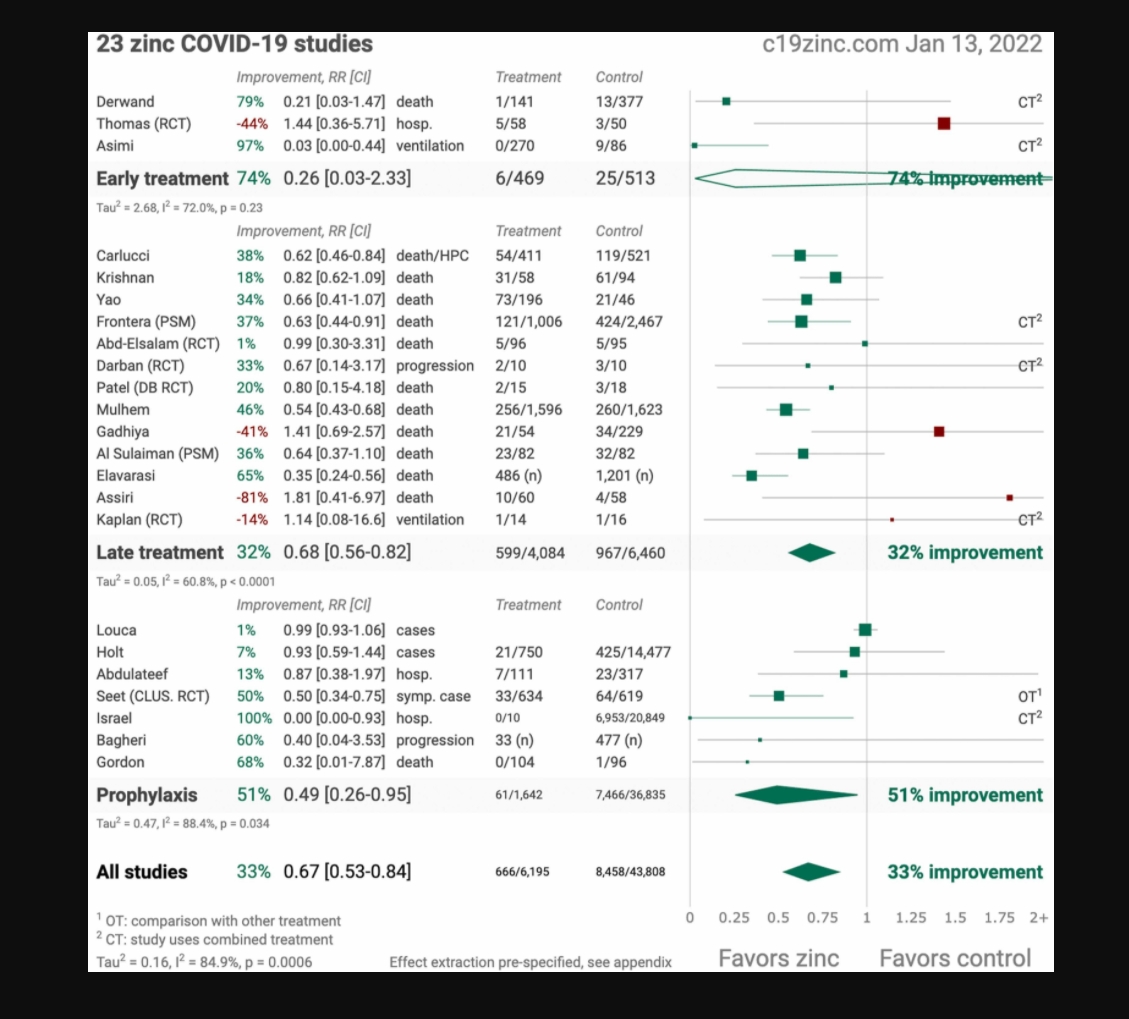
Zinc, is also known to be an important regulator of haemostasis and
thrombosis and deficiency has been implicated in haemorrhagic strokes (7).
Finally, all these micronutrients have the potential to protect against activation or relapse of
autoimmune conditions.
Vitamin D supplementation protects against aberrant autoimmune response
through modulation of the dendritic cells and other antigen presenting cells, to keep them
tolerogenic, and inhibition of Th1-type immune activity and suppression of B cells (key players in
autoimmune conditions) (8).
Selenium supplementation has been shown to protect against
autoimmune responses through a decrease in B cell activating factor (BAFF), increase in expression of
IL-10 in end-organ tissues and upregulation of B cell regulation and upsurges of T cell regulation.
Supplementation of both vitamin D and selenium is known to reduce and modulate disease activity
in autoimmune thyroid diseases (8,9). Zinc is known to play an important role in protection against
autoimmunity and low concentrations have been seen in autoimmune conditions (10).
Micronutrients exert an important role in the immune system and consequently could have a positive
impact on SARS-CoV-2 infection. We present an argument for addition of vitamin D, zinc and
selenium, relatively cheap and non-invasive supplements to prevent aberrant autoimmune reactions
and to prevent thrombosis. The target population will include individuals with nutritional deficiencies,
individuals, autoimmune conditions or individuals with a higher propensity towards developing
thrombosis.