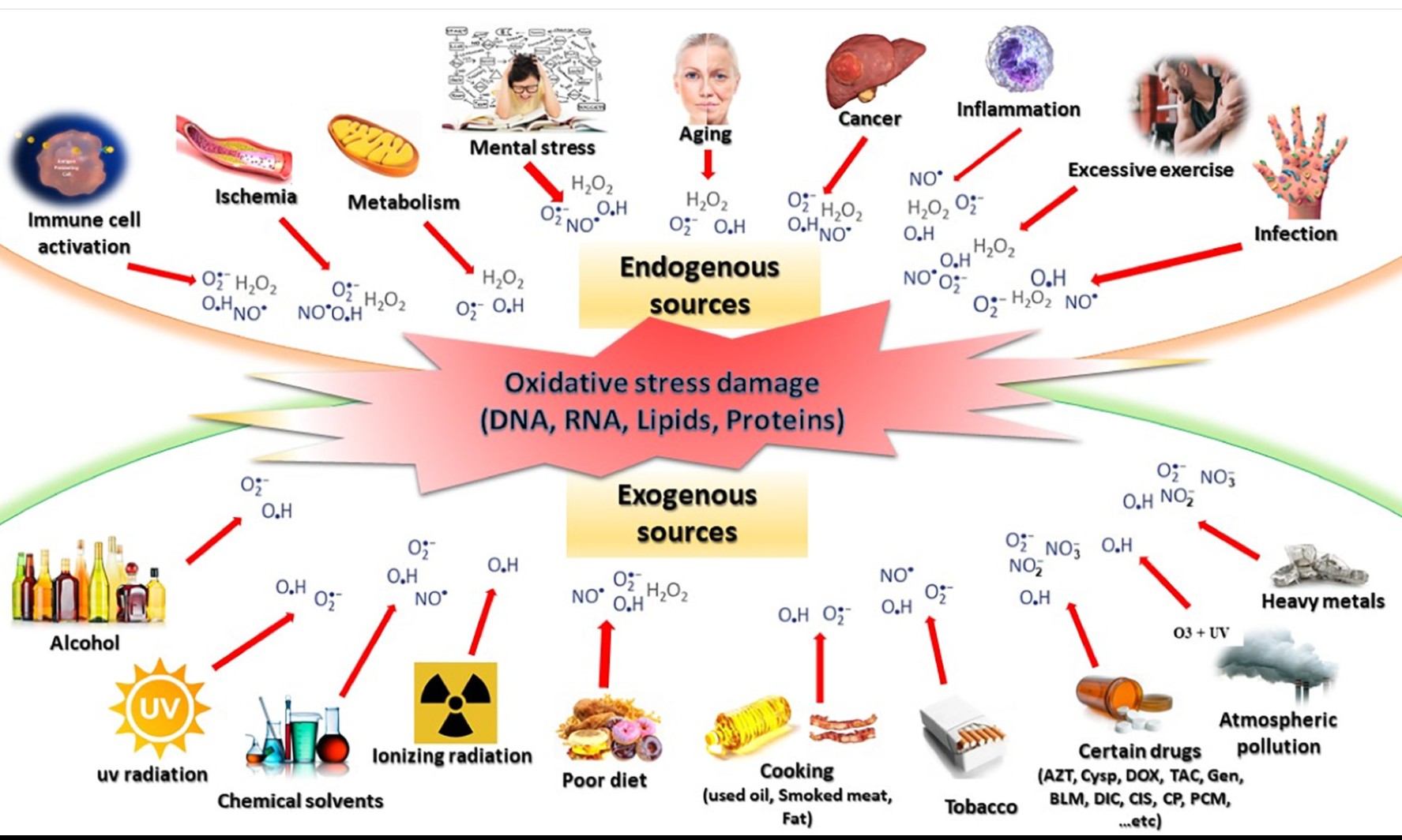
The impact of oxidative stress damage induced by the environmental stressors on COVID-19
Bianza Moise Life Sciences Volume 264, 1 January 2021, 118653
Highlights
• COVID-19 is associated with rising environmental stressors in stressed population.
• Chronic stressful events and malnutrition are likely to generate oxidative stress.
• Oxidative stress induces nucleic acid damage, leading to viral mutations.
• The viral mutants could compromise the impact of immune system and vaccine.
• COVID-19 management requires antioxidants, balanced diet, and healthy environment.
The ongoing pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a substantial stressor that is greatly impacting environmental sustainability. Besides, the different pre-existing environmental stressors and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)-related stressors are further worsening the effects of the viral disease by inducing the generation of oxidative stress. The generated oxidative stress results in nucleic acid damage associated with viral mutations, that could potentially reduce the effectiveness of COVID-19 management, including the vaccine approach. The current review is aimed to overview the impact of the oxidative stress damage induced by various environmental stressors on COVID-19. The available data regarding the COVID-19-related stressors and the effects of oxidative stress damage induced by the chronic stress, exposure to free radicals, and malnutrition are also analyzed to showcase the promising options, which could be investigated further for sustainable control of the pandemic.