Correlates of testosterone change as men age
Ricky Kanabar The Aging Male Volume 25, 2022 - Issue 1 Pages 29-40
Objective: The literature on testosterone (T) in men reports diverse correlates of T, some with minimal empirical support and most with little indication of how they change with advancing age. We test eight putative correlations across age.
Method: Correlations were tested on a large sample of British men.
Results: Seven of eight correlations replicated. Most change across men's life courses.
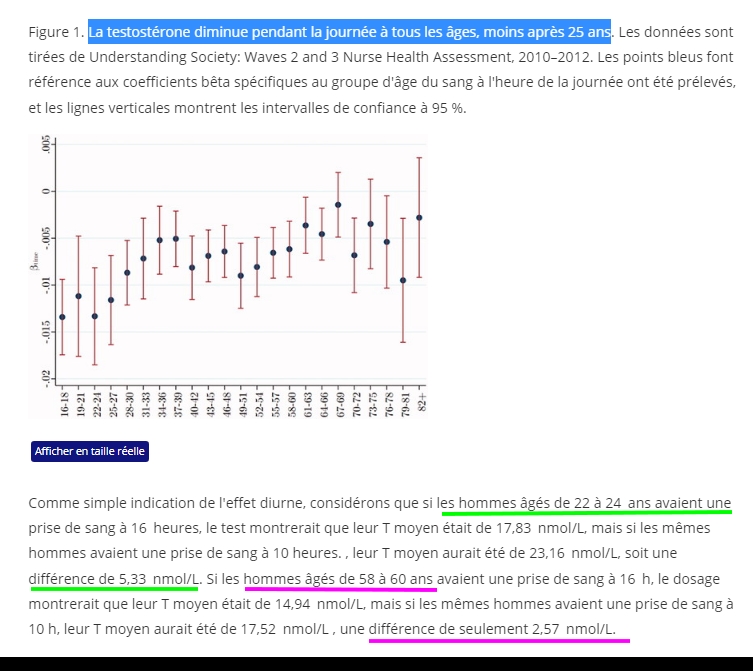
The diurnal cycle of T is considerably weaker among older than younger men.
Single men have higher T than married men of the same age; however, this difference lessens as men get older.
Elevated T among smokers is less pronounced as men age.
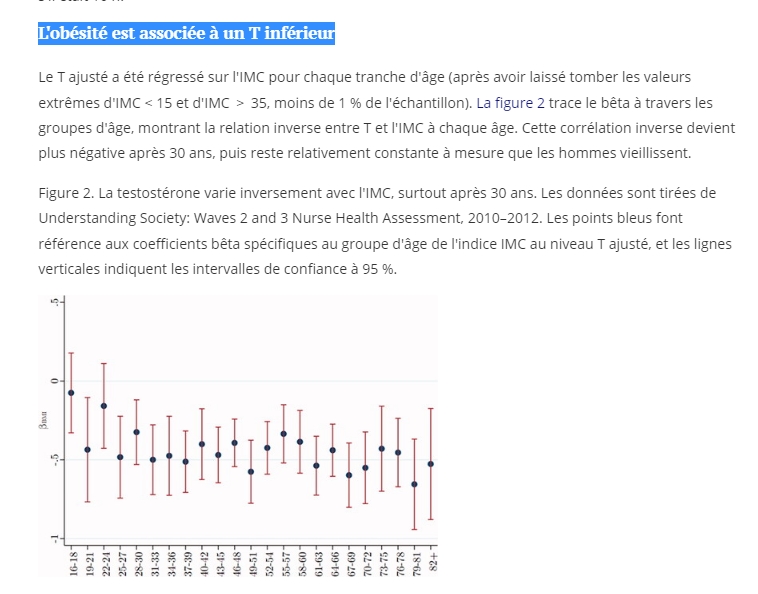
The inverse relationship between obesity and T is sustained across the adult age range.
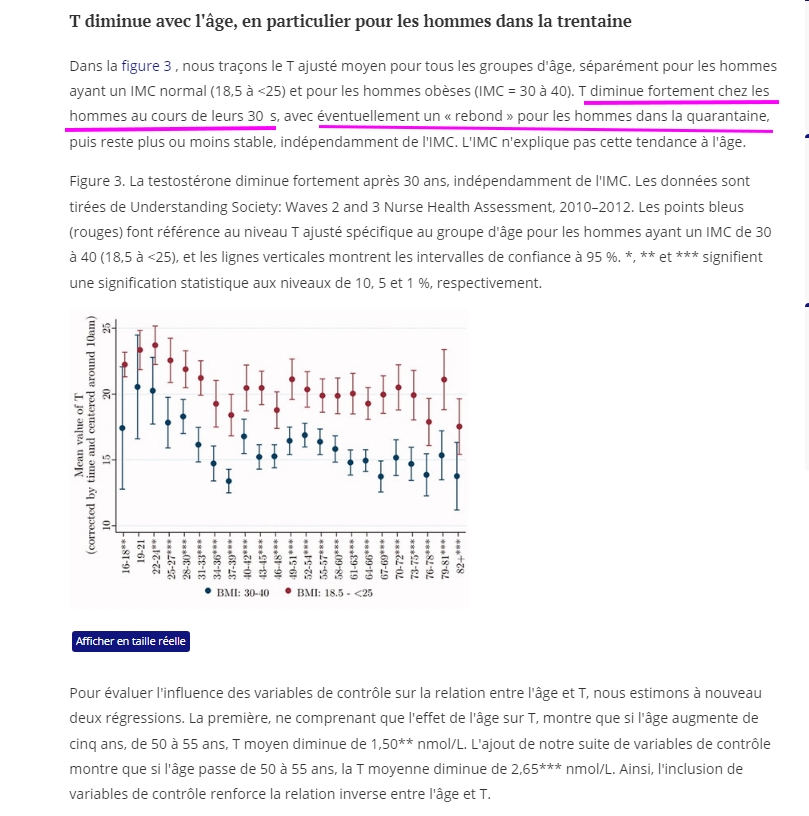
The lessening of T with age is well established, however there is disagreement about the course of decline. We find T having a steep decline around age 30, with possibly a rebound around age 50, after which levels remain roughly constant. Correlations involving health become stronger among older men. After age 30 or 40, the inverse relationships between T and HbA1c, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome all become increasingly significant, though not necessarily strong in magnitude.
Conclusion: Most putative correlates of T are replicated. There is a basis here for the generalization that among older men, those healthy have higher T than those who are not, but not a lot higher.