Over-expression of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy
Joseph J.Bass Molecular Metabolism 7 August 2020,
Highlights
• Increased Vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression stimulates skeletal muscle hypertrophy.
• Anabolic signalling, ribosomal biogenesis and muscle protein synthesis is enhanced.
• Coordinated upregulation of extracellular remodelling related gene-sets.
• VDR expression correlates with resistance exercise induced hypertrophy in humans.
Objective
The Vitamin D receptor (VDR) has been positively associated with skeletal muscle mass, function and regeneration. Mechanistic studies have focused upon loss of the receptor, with in vivo whole-body knockout models demonstrating reduced myofiber size and function, and impaired muscle development. To understand the mechanistic role upregulation of the VDR elicits in muscle mass/health, we studied the impact of VDR over-expression (OE) in vivo, before exploring the importance of VDR expression upon muscle hypertrophy in humans.
Methods
Wistar rats underwent in vivo electrotransfer (IVE) to over-express the VDR in Tibialis anterior (TA) muscle for 10 days, before comprehensive physiological and metabolic profiling to characterise the influence of VDR-OE on muscle protein synthesis (MPS), anabolic signalling and satellite cell activity. Stable isotope tracer (D2O) techniques were used to assess sub-fraction protein synthesis, alongside RNA-Seq analysis. Finally, human participants underwent 20-wks resistance exercise training, with body composition and transcriptomic analysis.
Results
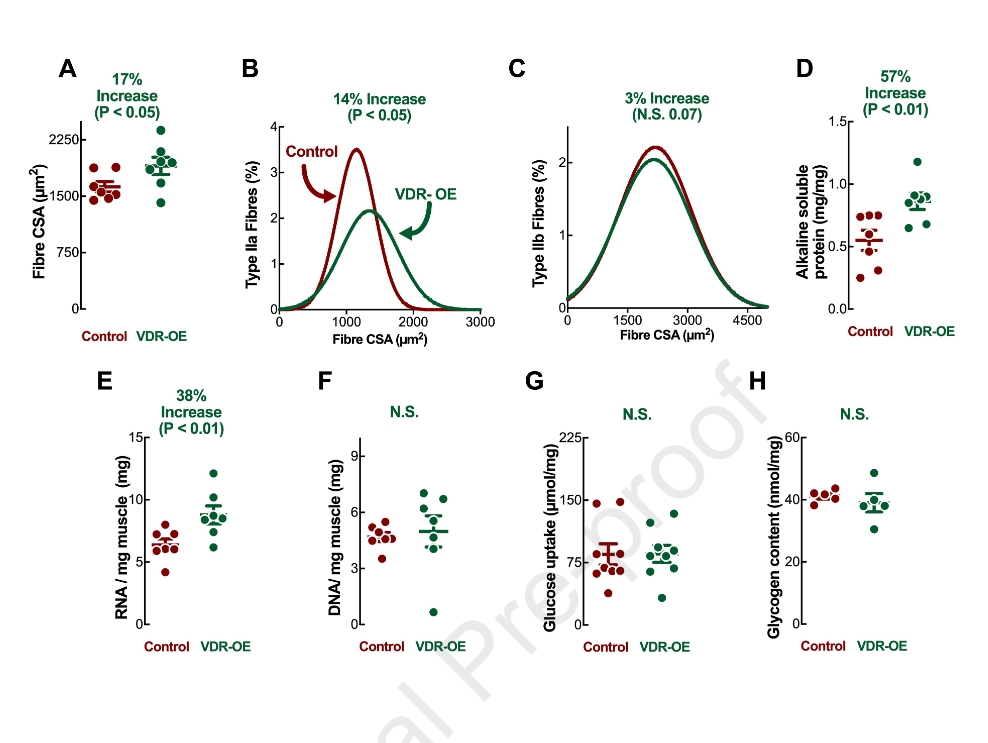
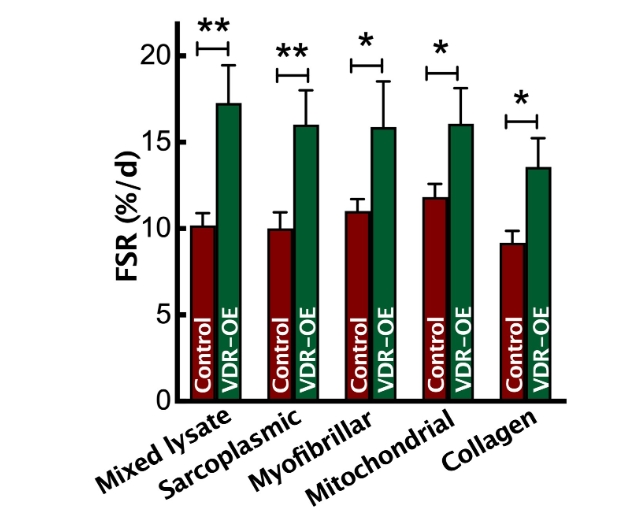
Muscle VDR-OE yielded total protein and RNA accretion, manifesting in increased myofibre area i.e. hypertrophy. The observed increases in MPS were associated with enhanced anabolic signalling reflecting translational efficiency (e.g. mTOR-signalling), with no effects upon protein breakdown markers being observed. Additionally, RNA-Seq illustrated marked extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, while satellite cell content, markers of proliferation and associated cell-cycled related gene-sets were up-regulated. Finally, induction of VDR mRNA correlated with muscle hypertrophy in humans following long-term resistance exercise type training.
Conclusion
VDR-OE stimulates muscle hypertrophy ostensibly via heightened protein synthesis, translational efficiency, ribosomal expansion and up-regulation of ECM remodelling related gene-sets. Furthermore, VDR expression is a robust marker of the hypertrophic response to resistance exercise in humans. The VDR is a viable target of muscle maintenance through testable Vitamin D molecules, as active molecules and analogs.