Effect of serum total testosterone and its relationship with other laboratory parameters on the prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in SARS-CoV-2 infected male patients: a cohort study
Selahittin Çayan The Aging Male 03 Sep 2020
Objective
To investigate effect of serum total testosterone and its relationship with other laboratory parameters on the prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infected male patients.
Methods
This prospective cohort study included 221 consecutive male patients (>18 years old) with laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 who had been hospitalized due to COVID-19. The patients were divided into 3 groups: Asymptomatic patients (n: 46), symptomatic patients who were hospitalized in the internal medicine unit (IMU) (n: 129), and patients who were hospitalized in the intensive care unit (ICU) (n: 46).
Results
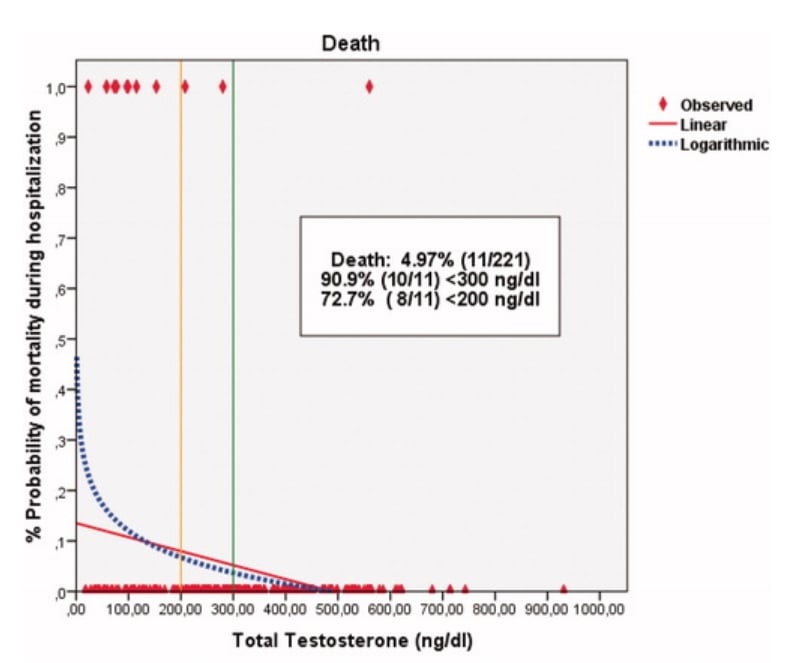
As serum total testosterone level at baseline decreases, probability (%) to be in the ICU significantly increases (p = 0.001). As serum total testosterone level at baseline decreases, probability (%) of mortality significantly increases (p = 0.002). In the patients who had pre-COVID-19 serum gonadal hormones test (n: 24), serum total testosterone level significantly decreased from pre-COVID-19 level of 458 ± 198 ng/dl to 315 ± 120 ng/dl at the time of COVID-19 in the patients (p = 0.003).
Conclusions
COVID-19 might deteriorate serum testosterone level in SARS-CoV-2 infected male patients.
Low serum total testosterone level at baseline has a significant increased risk for the ICU and mortality in patients with COVID-19.