Seasonal variation and trends in the Internet searches for losing weight: An infodemiological study
Ying Teng Obesity Research & Clinical Practice Volume 14, Issue 3, May–June 2020, Pages 225-233
Highlights
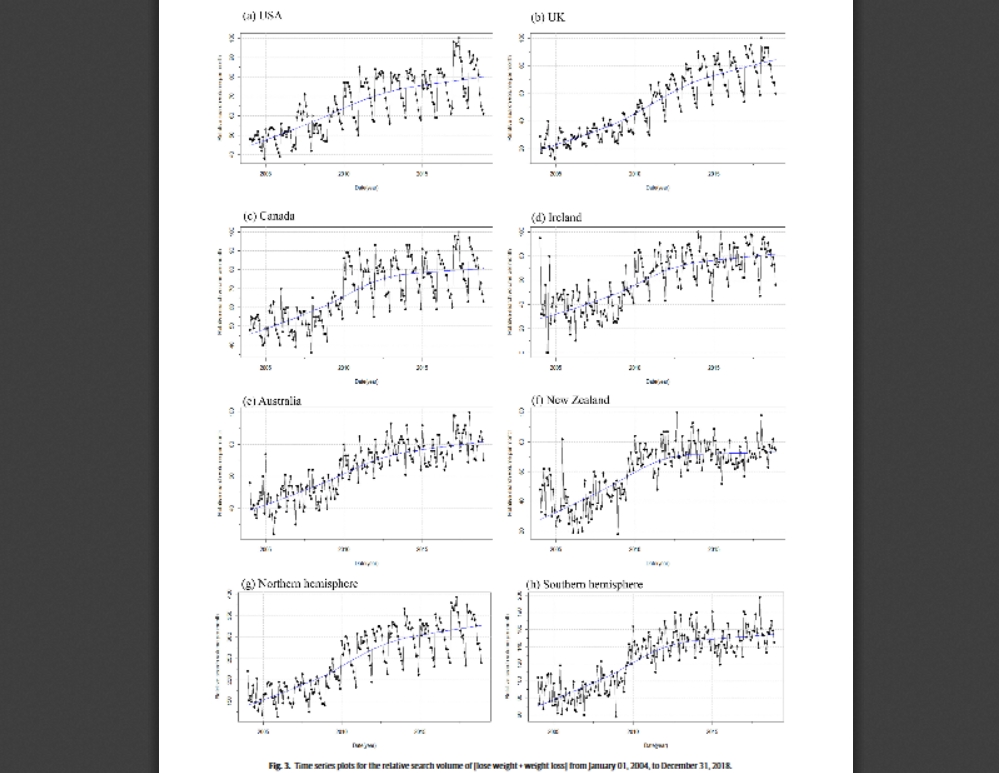
• Relative search volume for losing weight progressively increased from 2004 to 2018.
• The UK had the largest average increment speed for a search query of losing weight.
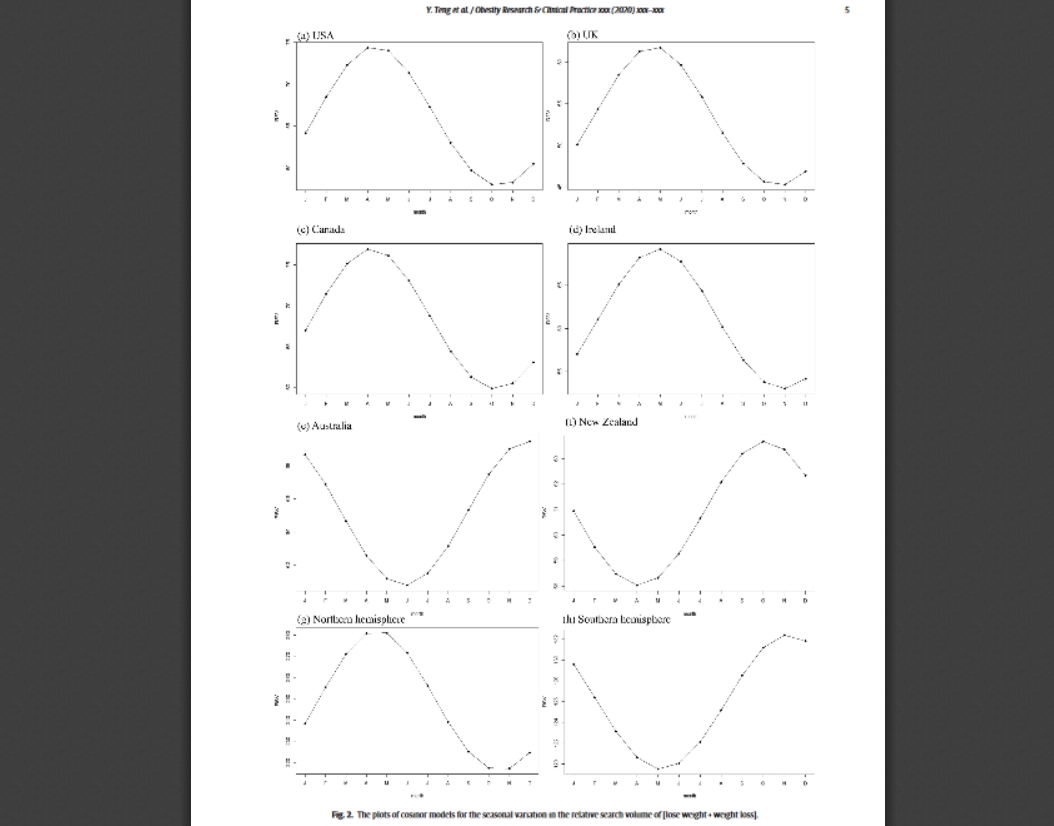
• There is a seasonality of losing weight with a peak in the spring months.
• A spike of relative search volume was observed in all countries in 2017.
Objectives
This study sought to examine the variation trends and seasonality of losing weight by using the data from Google Trends tool.
Methods
According to the search term of [lose weight + weight loss], Google Trends data were obtained. Search activity was conducted within the USA, the UK, Canada, Ireland, Australia, and New Zealand from January 01, 2004, to December 31, 2018, utilizing the health category.
Results
Dynamic series analysis and the plot of seasonal decomposition of time series show that relative search volume of [lose weight + weight loss] increased from 2004 to 2018 at both national and hemispherical levels. Statistically significant seasonal variations in relative search volume for the term [lose weight + weight loss] were observed using cosinor analyses in the USA (p < 0.001), the UK (p < 0.001), Canada (p < 0.001), Ireland (p < 0.001), Australia (p < 0.001), and New Zealand (p < 0.001), peaking in the spring months and reaching the lowest level in the autumn months. The highest level in spring and the lowest level in autumn were reversed by 6 months in both hemisphere countries, consistent with a seasonal pattern.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that Internet search queries for losing weight increased within the timeframe of 2004 to 2018, likely reflecting the rising global public interest. In addition, the present research provided preliminary evidence that there is a seasonality of losing weight with a peak in the spring months.