Dose-response effects of dietary protein on muscle protein synthesis during recovery from endurance exercise in young men: a double-blind randomized trial
Tyler A Churchward-Venne, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 112, Issue 2, August 2020, Pages 303–317,
Background
Protein ingestion increases skeletal muscle protein synthesis rates during recovery from endurance exercise.
Objectives
We aimed to determine the effect of graded doses of dietary protein co-ingested with carbohydrate on whole-body protein metabolism, and skeletal muscle myofibrillar (MyoPS) and mitochondrial (MitoPS) protein synthesis rates during recovery from endurance exercise.
Methods
In a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group design, 48 healthy, young, endurance-trained men (mean ± SEM age: 27 ± 1 y) received a primed continuous infusion of L-[ring-2H5]-phenylalanine, L-[ring-3,5-2H2]-tyrosine, and L-[1-13C]-leucine and ingested 45 g carbohydrate with either 0 (0 g PRO), 15 (15 g PRO), 30 (30 g PRO), or 45 (45 g PRO) g intrinsically L-[1-13C]-phenylalanine and L-[1-13C]-leucine labeled milk protein after endurance exercise. Blood and muscle biopsy samples were collected over 360 min of postexercise recovery to assess whole-body protein metabolism and both MyoPS and MitoPS rates.
Results
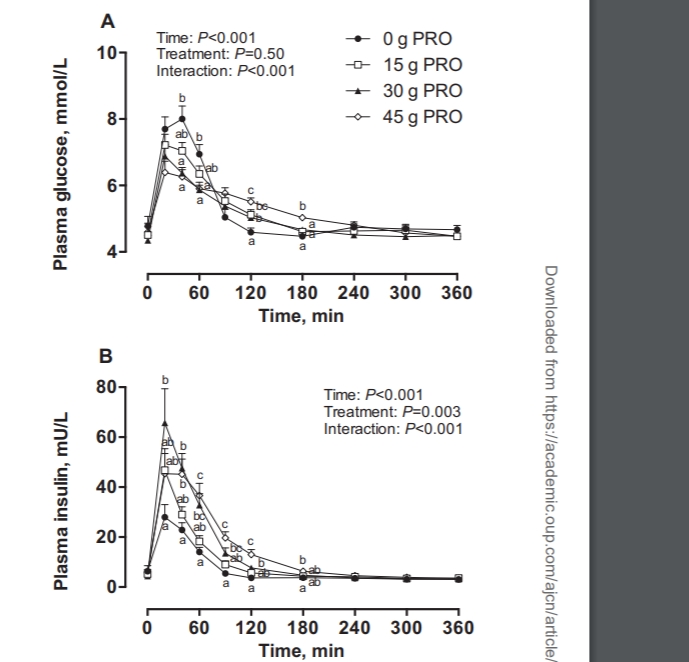
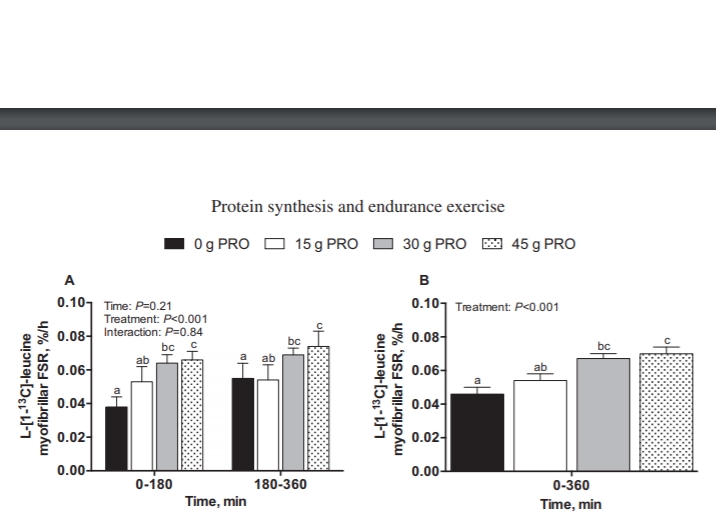
Protein intake resulted in ∼70%–74% of the ingested protein-derived phenylalanine appearing in the circulation. Whole-body net protein balance increased dose-dependently after ingestion of 0, 15, 30, or 45 g protein (mean ± SEM: −0.31± 0.16, 5.08 ± 0.21, 10.04 ± 0.30, and 13.49 ± 0.55 μmol phenylalanine · kg−1 · h−1, respectively; P < 0.001). 30 g PRO stimulated a ∼46% increase in MyoPS rates (%/h) compared with 0 g PRO and was sufficient to maximize MyoPS rates after endurance exercise. MitoPS rates were not increased after protein ingestion; however, incorporation of dietary protein–derived L-[1-13C]-phenylalanine into de novo mitochondrial protein increased dose-dependently after ingestion of 15, 30, and 45 g protein at 360 min postexercise (0.018 ± 0.002, 0.034 ± 0.002, and 0.046 ± 0.003 mole percentage excess, respectively; P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Protein ingested after endurance exercise is efficiently digested and absorbed into the circulation. Whole-body net protein balance and dietary protein–derived amino acid incorporation into mitochondrial protein respond to increasing protein intake in a dose-dependent manner. Ingestion of 30 g protein is sufficient to maximize MyoPS rates during recovery from a single bout of endurance exercise.