Gros plan sur la CarboxyMéthylCellulose ou CMC.
Votre protéine vous cache t'elle des choses
Lorsque l'on examine la composition d’une protéine en poudre, il est intéressant de commencer par la fin de la liste des ingrédients. C'est tout en bas que l'on trouve les substances ayant les noms les plus exotiques dont on peut s'interroger sur le pourquoi de leur présence.
En règle générale, plus la liste d'additifs est longue, plus il faut se méfier.
Pourquoi y a t-il de la CarboxyMéthylCellulose dans la whey ?
Les protéines en poudre comme la whey, sont assez insolubles dans un liquide (eau ou lait). Si on les secoue avec un shaker, elles se mettent à mousser de manière importante.
On peut forcer la whey à bien se dissoudre dans l'eau sans mousser en lui ajoutant un gel synthétique (CarboxyMéthylCellulose) et un surfactant (le plus souvent un extrait de soja) qui attire l'eau. La combinaison du surfactant et de la CarboxyMéthylCellulose (CMC) permet d’obtenir une whey parfaitement soluble.
Le consommateur a l'impression que cette whey est de très grande qualité car elle fond littéralement dans l'eau.
Très bien, mais à quel prix pour la santé de l'utilisateur
Comment la perturbation intestinale se produit-elle ?
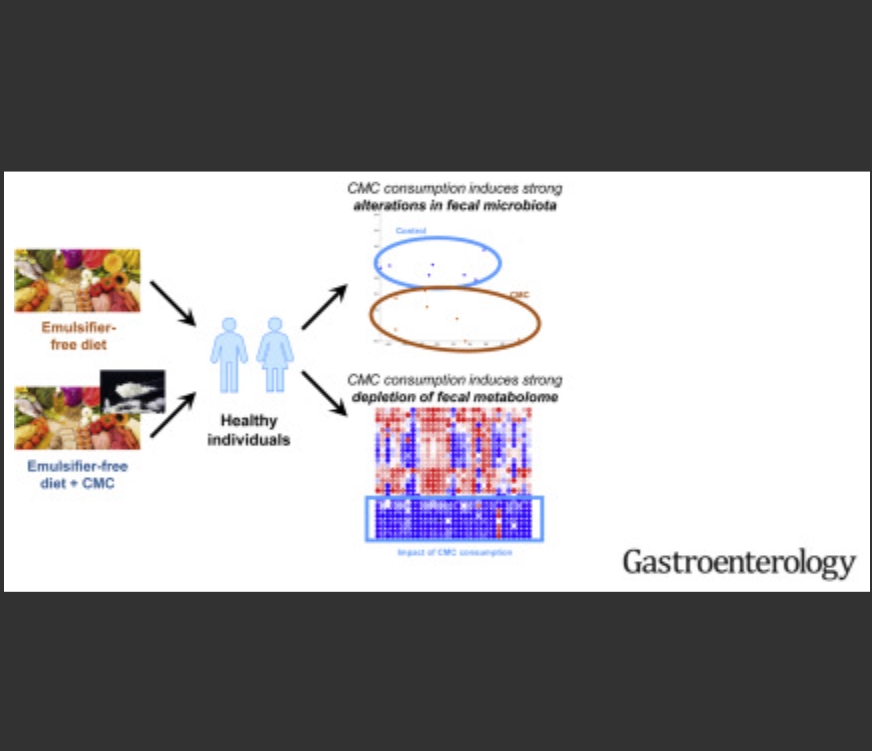
Un épais mucus qui agit comme une barrière de protection sépare les bactéries de l'intestin lui-même. Les bactéries intestinales n'ont donc pas accès aux cellules de l'intestin. La CarboxyMéthylCellulose (CMC) qui agit comme un détergent (on en met dans les lessives pour cela) procure cet accès aux bactéries. Ces dernières attaquent directement les cellules intestinales provoquant une inflammation chronique.
Un autre effet de la CMC est d’altérer la composition de la flore intestinale en augmentant la concentration des bactéries pathogènes et moins favorables à une bonne santé.
Les chercheurs (1) pensent que l'inflammation chronique du système digestif pousse les gens à manger trop ce qui facilite la prise de graisse.
Les limites de l'étude
Il faut préciser que l'ajout de CarboxyMéthylCellulose (CMC) dans la nourriture est tout à fait autorisé comme additif alimentaire. Elle se cache aussi sous l’appellation E466.
Les défenseurs de la CMC expliquent que cette étude ne concerne que des doses élevées de CMC qui correspondent à 150g de CMC par jour.
Cependant, même si nous ne consommons pas autant de CMC que dans l'étude, nous en consommons toute notre vie.
Si votre protéine est "enrichie" à la CarboxyMéthylCellulose (CMC), vous consommerez de la CMC tous les jours, voire plusieurs fois par jour et ce, pendant des années. Vous serez donc constamment exposés à de la CMC. Celle-ci s'ajoutera à la CMC que l'on retrouve dans de nombreux aliments préparés.
Pour l'anecdote, les produits pauvres en gluten sont souvent "enrichis" en CMC car il faut bien compenser d'une manière ou d'une autre les effets culinaires qu'apporte le gluten dans les plats ou les aliments préparés. Les vignerons en mettent aussi dans le vin, ...
La position de Nutrimuscle sur l'ajout de CarboxyMéthylCellulose aux protéines
Depuis toujours, Nutrimuscle a refusé d'ajouter de la CarboxyMéthylCellulose (CMC) dans ses protéines et plus largement dans tous ses compléments alimentaires. Nutrimuscle garantit donc l'absence de CMC dans ses suppléments nutritionnels.
En conséquence, les whey Nutrimuscle moussent plus que les whey "trafiquées" à la CMC mais le consommateur ne prend pas de risque inutile pour sa santé.
Référence scientifique
(1) Chassaing B. Dietary emulsifiers impact the mouse gut microbiota promoting colitis and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2015 Published online 25 February 2015

Bon choix.
Bien à vous.