Melatonin and its derivative contents in tropical fruits and fruit tablets
Journal of Food Composition and Analysis Volume 103, October 2021, 104109 Thorung Pranil
Highlights
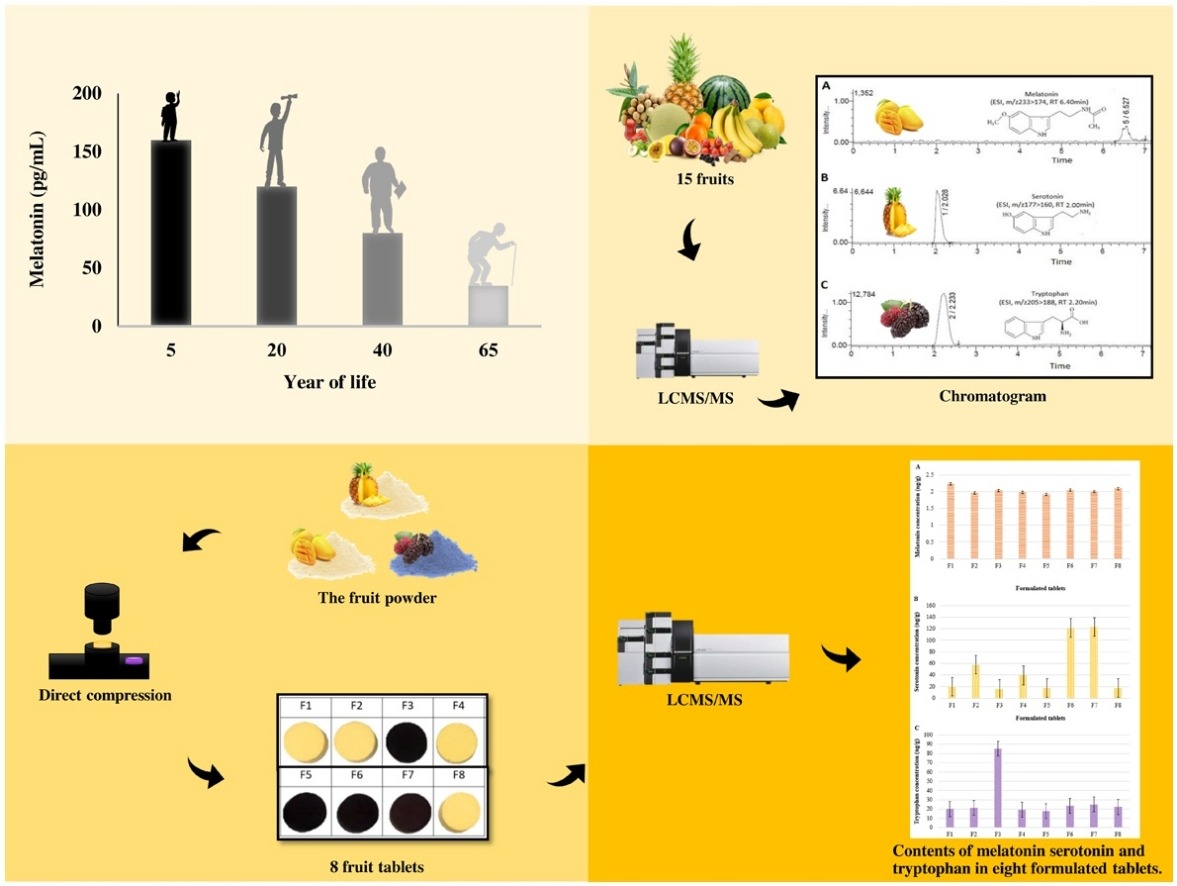
• Melatonin had the highest contents in mango.
• High serotonin and tryptophan levels were detected in pineapple and mulberry.
• Serotonin level in tablets increased at higher pineapple and mulberry percentages.
• Mulberry tablets recorded the highest tryptophan concentration.
Melatonin is a hormone that controls the human circadian rhythm and also protects plants against severe stress conditions. Recently, melatonin has been used for immunomodulatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer health purposes. However, scant information concerning tropical fruit contents of melatonin and its derivatives is available. Melatonin, serotonin, and tryptophan contents in fifteen tropical fruits were determined using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). Melatonin concentrations in Thai fruits varied from 1.528 to 2.401 ng/g dw, with highest levels of melatonin, serotonin, and tryptophan detected in mango, pineapple, and mulberry (2.401, 68.092, and 175.527 ng/g dw, respectively). Fruit tablets rich in melatonin and its derivatives were also developed from selected fruits including mango, pineapple and mulberry.
Mango tablets were high in melatonin (2.24 ng/g dw). Increasing pineapple and mulberry percentages in the tablets significantly improved the serotonin level, while mulberry tablets contained the highest tryptophan level. Serotonin content in mixed fruit tablets containing mango, pineapple and mulberry or mixed pineapple and mulberry were higher than in individual fruits. Results can be used as guidelines to determine the concentrations of melatonin and its derivatives. Our findings can also be used to construct a database for melatonin, serotonin, and tryptophan contents in fruits and estimate their potential contribution to dietary requirements.