Omega 6/omega 3 fatty acid ratio as an essential predictive biomarker in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Shilpa. S.Shetty Nutrition Available online 7 August 2020,
Highlights
• Total saturated fatty acids (SFA's) (palmitic and stearic) were higher in the diabetic group.
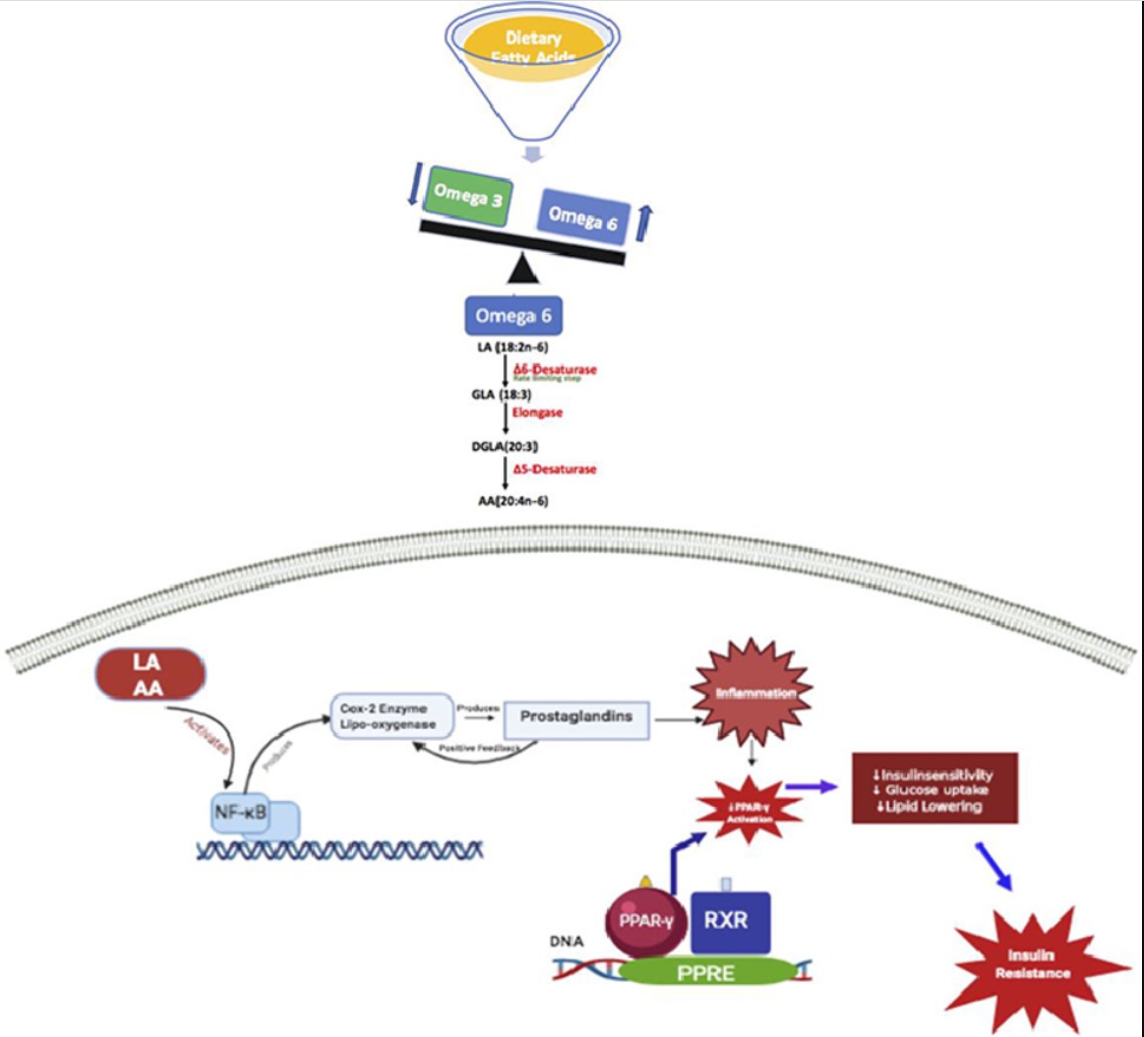
• Omega-3 (n-3) PUFA was inversely associated with risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus whereas omega-6 (n-6) PUFA showed a direct association.
• Omega 6/ omega 3 ratio showed a positive correlation with fasting blood sugar, insulin, glycated hemoglobin and insulin resistance.
• Multivariate model with D5D, D6D and omega 6/omega 3 ratio served as the best predictive model for the association of omega pathway with diabetes.
Background
Dietary fatty acid intake may play a major role in the prevention and management of lifestyle related diseases, like type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Therefore, the present study aims to find an association between omega 6/omega 3 ratio and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methodology
Fasting plasma glucose, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and insulin were measured using commercially available kits. Fatty acid methyl esters were prepared using standard protocols. Delta 5 desaturase (D5D) and delta 6 desaturase (D6D) activities were determined from product-to-precursor ratios of individual fatty acids in plasma. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 20.0.
Results and Discussion
Omega 6/omega 3 ratio was higher in the diabetic group (13:1) when compared to that of the non-diabetic group (4:1) and was statistically significant (p<0.0001). Further association studies, showed that univariate model with omega 3/omega 6 ratio and a multivariate model with D5D, D6D, and omega 6/omega 3 ratio could serve as predictive PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acid) pathway models for T2DM.
Conclusion
From the study results, it is evident that omega 6/omega 3 fatty acid ratios can serve as an essential predictive biomarker in the management of T2DM. This would not only help in management but also in prevention of increased type 2 diabetes incidence in India. Thereby potentiates the need to maintain an ideal balance of omega 6/ omega 3 ratio as prevention is always better than cure.