Association between skipping breakfast and risk of cardiovascular disease and all cause mortality: A meta-analysis
Hanze Chen Clinical Nutrition Volume 39, Issue 10, October 2020, Pages 2982-2988
Background & aims
Previous studies on the association between skipping breakfast and risk of cardiovascular disease and all cause mortality have drawn controversial conclusions. Therefore, we carried out a meta-analysis to illuminate this association.
Methods
Studies about the association between skipping breakfast and risk of cardiovascular disease and all cause mortality were identified by searching Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane, and Web of Science databases until June 2019. Then we screened articles for eligibility, extracted data, and pooled the results using a random-effects model.
Results
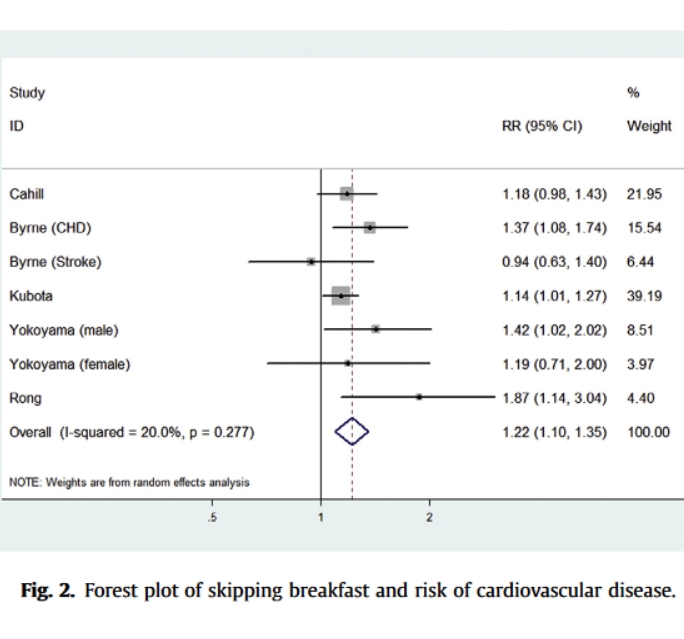
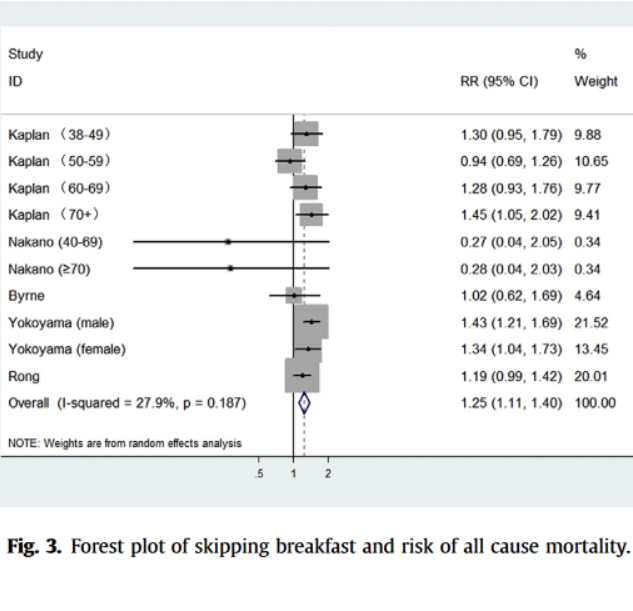
Seven cohort studies concerning a total of 221,732 participants were included in this meta-analysis. Skipping breakfast was associated with elevated risk of cardiovascular disease (relative risk 1.22 95% confidence interval 1.10–1.35) and all cause mortality (relative risk 1.25 95% confidence interval 1.11–1.40) compared with eating breakfast regularly.
Conclusion
Skipping breakfast increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and all cause mortality. Eating breakfast regularly may promote cardiovascular health and decrease all cause mortality.